Introduction
Lean Six Sigma is a powerful methodology that combines the principles of Lean management and Six Sigma to drive process improvement and minimize waste.
This powerful approach helps you bridge the gap between where you are and where you want to be, streamlining processes and minimizing errors for peak project performance.
Let’s explore Lean Six Sigma in project management in detail. We will dive deep, from defining its core principles to uncovering its benefits and limitations.
But before moving ahead, let’s understand Lean Six Sigma first.
What is Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is a methodology that helps organizations improve their processes and quality. Lean focuses on eliminating waste and making operations more efficient, and Six Sigma aims to reduce variation and defects. Together, they provide tools to help businesses work better and satisfy customers more.
What is lean?
Lean project management focuses on eliminating eight types of waste in processes. Waste refers to any activity that consumes resources but doesn’t add value to the final deliverable. This could be anything from unnecessary meetings to redundant approval processes.
Project Management Institute defines Lean as, “To be Lean is to provide what is needed when it is needed, with the minimum amount of materials, equipment, labor, and space.”
It was originally developed by the Toyota Production System (TPS) in the late 1940s. It continued to evolve and refine up till the 1980s. The implementation led to reduced costs, improved performance, and optimal efficiency.
What is Six Sigma?
Six Sigma methodology is driven by minimizing defects and process improvement through a data-driven approach. It emphasizes identifying and eliminating the root causes of errors to achieve near-perfect project execution. Six Sigma uses statistical analysis to pinpoint variations and measure the effectiveness of solutions.
Six Sigma summed up by PMI Institute – “The Six Sigma method focuses on understanding customers’ requirements better and eliminating defects and waste. These objectives are achieved through profound knowledge of statistics, engineering, and project management, as well as the underlying processes and systems.”
Motorola pioneered Sigma principles in 1986, and it continued till it was widely recognized in 1992 by General Electric (GE). It is widely adopted across many organizations and industries to improve quality, save money, and decrease defect rates.
Overall, the combination of the two results is Lean Six Sigma.
As per the definition provided by the American Society for Quality (ASQ),” Lean Six Sigma is a fact-based, data-driven philosophy of improvement that values defect prevention over defect detection.”
Lean acts as the detective, spotting any unnecessary bumps in your project flow. Six Sigma then jumps in as the fixer, using data and clever solutions to smooth out those bumps and get your project back on track.
Lean Six Sigma project management methodology
The Lean Six Sigma methodology complements project management by eliminating unnecessary waste and defects from the processes. This improvement further extends to increasing efficiency, streamlining processes, and achieving some fundamental improvements in operational processes.
The core framework of implementing the Lean Six Sigma methodology is DMAIC and DMADV.
DMAIC
DMAIC is a five-phase method—Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control, and is a problem-solving approach to process improvement.
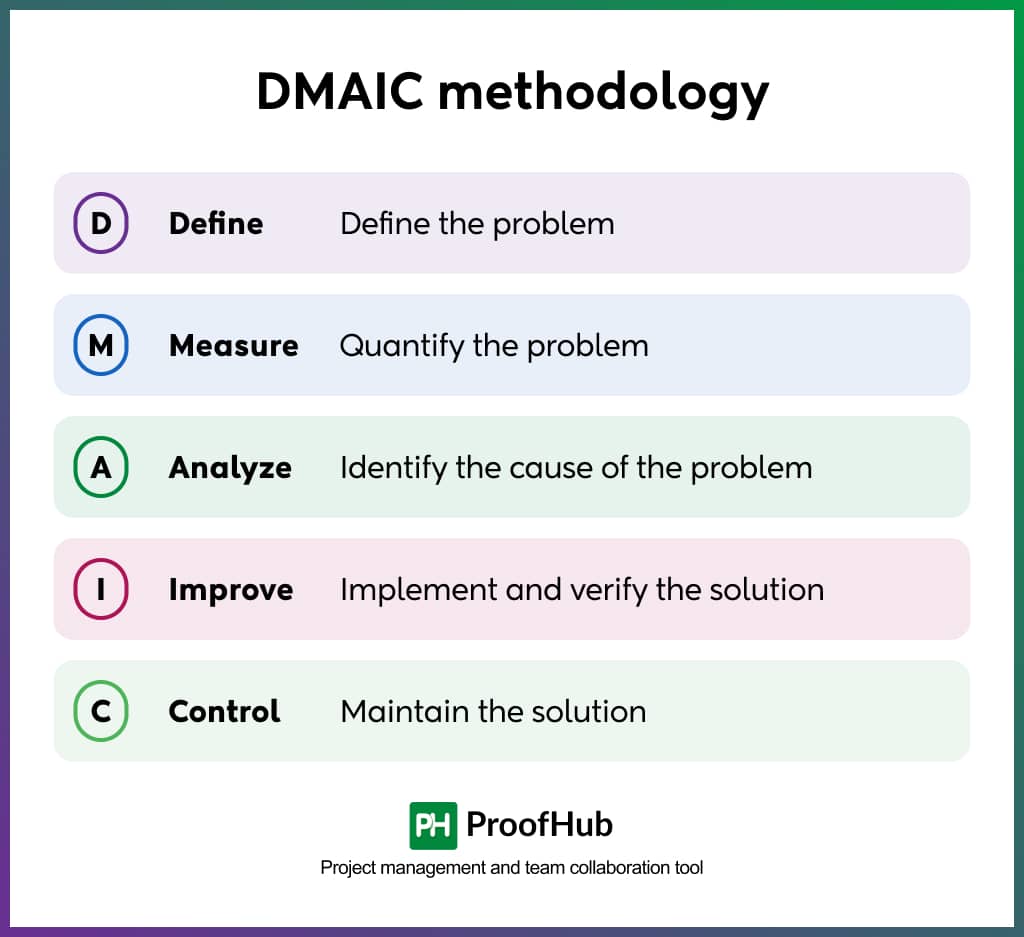
1. Define
Outline the most value-driven opportunities and possibilities for improvement. Map out all the value-driven elements, focus, scope, issues, and ultimate goals. Determine the performance standard that will highly impact customer satisfaction. Defining these parameters ensures your team shares the same vision.
2. Measure
Draw out project baselines to assess the current performance of your project. This acts as a benchmark measurement against which you can evaluate the effectiveness of implemented improvements. By collecting historical data, customer feedback, and metrics, you can view your goals through a contextual lens.
3. Analyze
Aim to uncover all the possible root causes of the underlying problem. These are the potential factors that contribute to the variation in your process, and end up costing you time, resources, and money. You can visualize these factors by utilizing data visualization tools like Kanban board, Gantt charts, etc.
4. Improve
When all the issues are in front of you, start developing and implementing your functional process improvement plan. You should incorporate team suggestions, brainstorm solutions, and iterate to obtain the optimal solution to eradicate the issue. You can even test your solution to validate the optimal outcomes.
5. Control
Monitor the implemented solutions to ensure sustained improvement of your process. Continually evaluate the improvised processes to look for unusual occurrences and adjust the approach accordingly. Also, to be on the safer side, ensure a response plan is in place to address discrepancies continually.
DMADV
DMADV is also a five-phase method – Define, Measure, Analyze, Design, and Verify. This is used for developing new processes, products, and services that meet customer requirements. It is useful when the existing process is not useful and needs to be updated from the start.
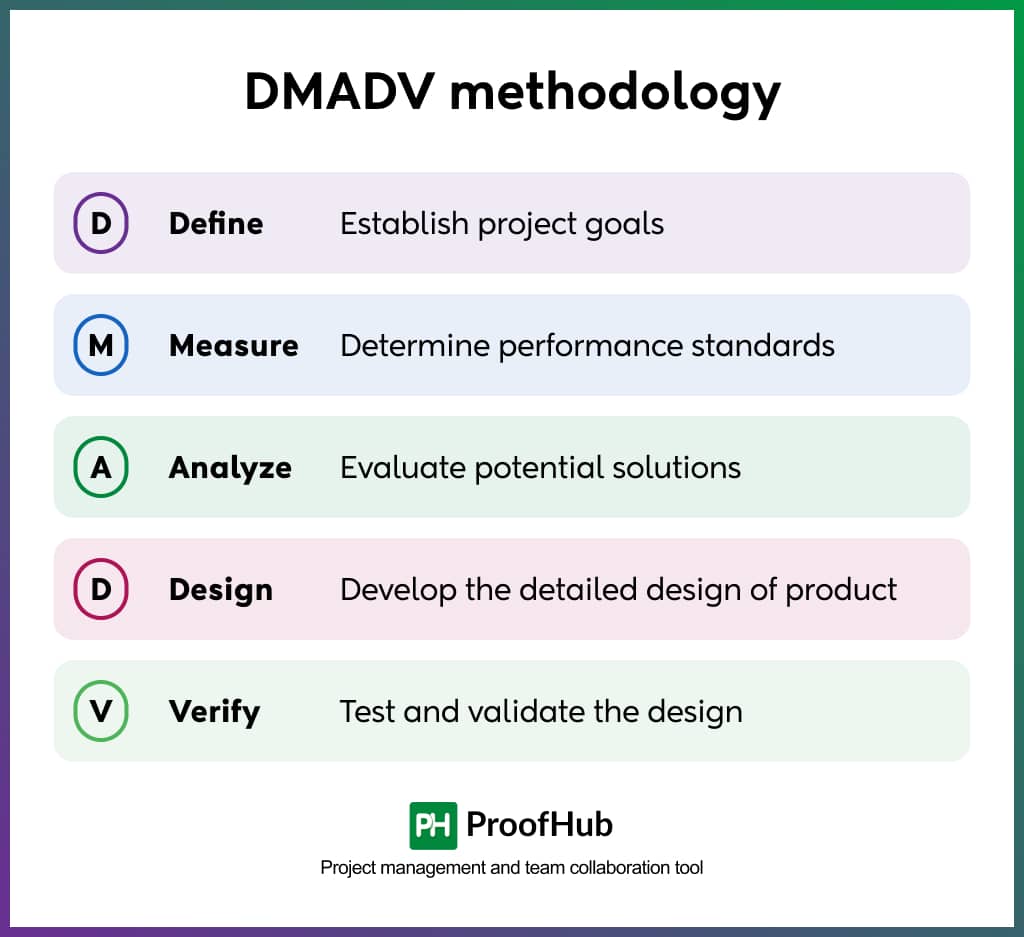
1. Define
In the Define phase, the project goals are established and aligned to the customer’s needs. This is the most crucial stage because this is the foundation of the whole project.
2. Measure
This phase focuses on identifying the critical-to-quality characteristics that impact customer satisfaction. These can be related to performance, reliability, or any other quality that the customer values.
3. Analyze
In this phase, the potential solutions or designs are explored and evaluated based on customer needs and project requirements.
4. Design
In the Design phase, the selected solution or product is developed in detail. This stage involves creating a complete design that meets customer needs and requirements while minimizing variability.
5. Verify
The Verify phase is about making sure the design works as it should and meets customer needs and project goals. This is the last check before full-scale implementation.
Lean Six Sigma principles
Lean Six Sigma (as stated above) is a powerful blend of two methodologies. It has five key principles that help organizations achieve operational excellence and predictable project outcomes.
Let’s understand each principle one by one:
1. Customer focus
Companies that prioritize customer experience, witness an 80% increase in their revenue.
And LSS’s principles align perfectly with the trend. That is why its ultimate goal is to deliver value-driven products to customers. This highlights the importance of prioritizing customer needs, satisfaction, and expectations over anything else. That is why, customer feedback is given high priority when refining processes and implementing projects.
2. Data-driven decision-making
Learn Six Sigma doesn’t go vague when it comes to making decisions to improve processes. Instead, you can utilize a statistical analysis of project data insights to improve process effectiveness. By using historical data, current metrics, and various key performance indicators, you can guide process improvement efforts accordingly.
3. Continuous improvement
LSS is a continual improvement process that promotes sustained improvements. Teams are encouraged to not settle for desired output achievement. But to always strive for better project outcomes. So, multiple evaluations and adjustments are performed to ensure the project’s sustainability over time.
4. Teamwork
The zero-waste ideology of Lean Six Sigma is a team-based strategy. It brings employees from all levels, functions, and departments together to share their diverse perspectives. This results in increased employee engagement levels and enhanced knowledge sharing.
5. Process optimization
The prime goal of LSS is to improve process efficiency and quality by eliminating waste and reducing variations. The improvement strategies are designed to eliminate inefficiencies, ensure smoother operations, and enhance quality production.
When should you use Lean Six Sigma in project management?
No doubt, Lean Six Sigma possesses substantial strengths. But it is not applicable in every scenario
Consider implementing LSS only if you want to
- Eliminate defects and inefficiencies from your processes
- Standardize repetitive projects with well-defined stages
- Increase employee engagement and morale
- Enhance customer experience and satisfaction
- Deliver high-quality results
- Introduce data-driven strategies
- Reduce operational costs caused by rework and delays
Do not consider adopting LSS if
- Your project faces a tight deadline. As LSS is a time-consuming concept.
- You lack access to historical data and cannot stay abreast of current trends.
- You oversee novel or one-time projects with unique requirements and conditions
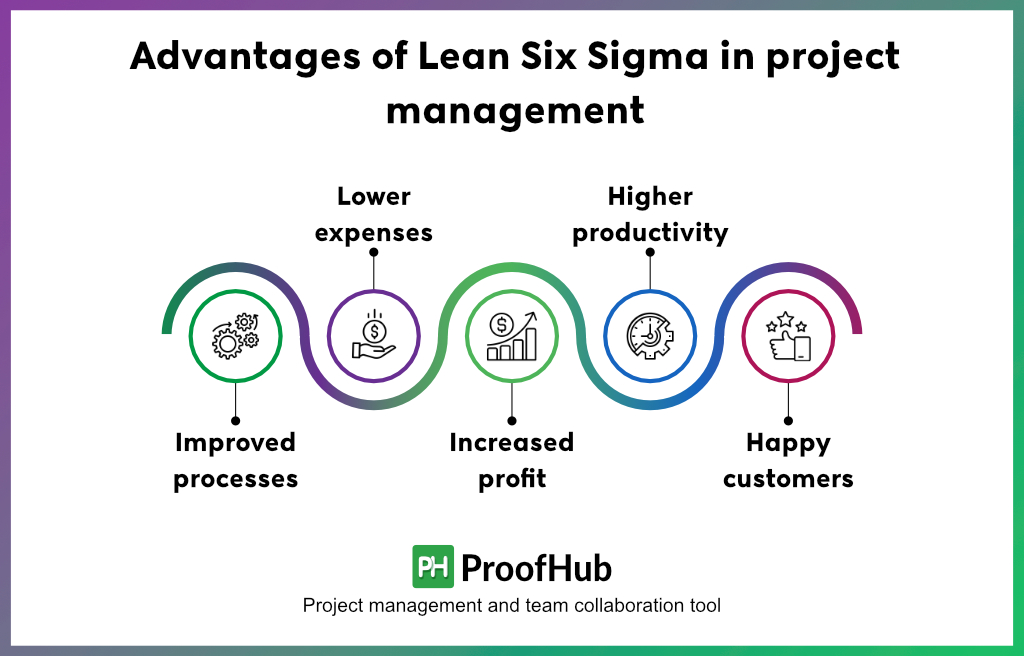
Advantages of Lean Six Sigma in project management
By optimizing your business processes using LSS, you get:
1. Improved processes
LSS is more of a problem-preventing approach than problem-solving. It eliminates non-value-added activities, variations, and delays in processes. This results in faster project completion with less time, resources, and wasted materials.
2. Lower expenses
With no waste and defect-free activities to impact your processes, companies can save a significant amount of money in each process cycle. Also, companies can avoid costly inspection-and-rework cycles by embracing a ‘defect prevention’ ideology.
3. Increased profit
By applying a systematic approach to life-cycle assessments, LSS streamlines and accelerates product delivery. Companies can leverage this approach to achieve higher bottom-line results and maximize ROI.
“Companies have saved millions of dollars with this (LSS) approach and anyone can do it.” – Bob Myers, Lean Six Sigma Black Belt, Lecturer in Operations Management at the Georgia Tech Scheller College of Business.
4. Higher productivity
The zero-defects ideology of LSS frees up employees for the core tasks that matter. Also, with minimal bottlenecks in processes, employees can focus more on attaining the organizational vision. This efficiency leads to faster task completion and delivery.
Amp up your productivity levels using top productivity tools
5. Happy customers and employees
Both employees and customers are the two strong pillars of an organization. By delivering high-quality projects and improving operational efficiency, you benefit both categories. Where employees gain positive work experiences through streamlined processes, customers feel satisfied as their needs are met efficiently and effectively.
How can project managers benefit from Lean Six Sigma?
Lean Six Sigma is one of the project management skills that project managers aspire to acquire. But not every project manager is equipped with the same.
However, if you choose to strengthen your command in Lean Six Sigma, you can benefit in several ways:
- It helps you identify the most beneficial aspects that provide the most value to the organization.
- By aligning diverse perspectives and talents toward achieving shared goals, managers can create a collaborative environment.
- Your problem-solving skills advance as you look for effective solutions to eliminate waste and defects.
- It enhances your ability to identify and deal with risks by empowering your strength to tackle unforeseen challenges.
- LSS helps you create a culture of autonomy where everybody is empowered to mitigate potential errors and variations.
However, Lean Six Sigma managers can avail of all these benefits to the fullest only when they have Lean Six Sigma project management certifications.
Add value to your role by getting yourself these top project management certifications
Examples of Lean Six Sigma projects
Lean Six Sigma isn’t just theory. It has a proven track record of success across industries.
Let’s just first take an example of how LSS brought us some big-time improvements, defining other examples later on –
1. Software development with ProofHub
It all started when some crazy challenges were impacting our software development processes – long development cycles, missed deadlines, irked clients, and constant bugs.
Recognizing the urgency, we turned to Lean Six Sigma methodology, teaming it up with the robust capabilities of ProofHub, to streamline our development process. It facilitated:
- Collaboration: Streamlined communication and knowledge sharing between team members using collaborative real-time features like chat, discussion, and @comments.
- Data visibility: Real-time insights into project progress and performance metrics with multiple task views including board view, Gantt chart, table view, and more.
- Actionable planning: Enabled efficient task assignment and streamlined workflow management using its robust task management features.
- Continuous monitoring: Facilitated ongoing data analysis and adjustments using reports to maintain process improvement.
The results? A significant reduction in our release cycle time and rework due to improvised solutions.
2. Manufacturing
- Honeywell: This aerospace products and services giant leverages Lean Six Sigma in its operations under the name Six Sigma Plus. It helped them obtain significant financial benefits. Along with some added advantages over their supply chain, product design, manufacturing, growth, etc.
3. Finance
- Bank of America: This major financial firm integrated Lean Six Sigma to optimize operational efficiency and elevate its performance benchmarks. Implementing this methodology, they witnessed significant improvements in their deposit processing, customer delight metric, etc.
By focusing on data-driven decision-making, they were able to streamline processes and achieve significant improvements.
4. Exploration
- Chevron: Another standout example from the success stories of Lean Six Sigma is Chevron – an oil and gas company. They primarily focussed on optimizing internal efforts, later on expanding it to its supply chain.
Boston Strategies International (BSI) awarded Chevron stating, “The initiative has reduced average drilling time, reduced workover rig cycle time, and reduced the lead time for engineering drawings.”
These are just a few examples of Lean Six Sigma wins. You name the industry, and LSS is operational there.
Limitations of Lean Six Sigma in project management
LSS, despite its effectiveness, is not without drawbacks. Here are a few of them:
- Complex in nature
Lean Six Sigma is quite intricate because it requires managers to have prior procedural knowledge of two methodologies – Lean and Six Sigma. Not having the right training and development opportunities in either of the two can lead to frustration and inefficiency.
- No one-size-fits-all solution
If you think every project can be addressed with LSS, then you are wrong. You need to invest a considerable amount of time to analyze and evaluate the processes that may yield profitable results when integrated with LSS.
- Emphasize established procedures
The entire LSS framework focuses on optimizing the existing processes. So, any new projects or processes can not benefit substantially from its implementation.
- Additional resource consumption
While no doubt Lean Six Sigma aims to reduce costs to businesses. But the investment that goes into training and educating your employees in the first place is quite significant. You can not even overlook the factor because the acquired knowledge is substantial enough to operate efficiently.
- No quick results
LSS is a time-intensive process that requires an average of two years to reflect tangible results in the process. This is a huge timeframe for companies that want quick improvements. So, if you are seeking immediate results, do not consider wasting your efforts and talent in LSS.
What are the levels of Lean Six Sigma
The levels of Lean Six Sigma refer to the different certification belts that one can achieve. These levels are referred to as “belts” in a hierarchical system similar to martial arts, and each level corresponds to a certain level of skill and responsibility in process improvement projects.
1. White Belt: Basic understanding of Lean Six Sigma concepts and terms, and often helps teams in small roles.
2. Yellow Belt: Help project teams solve smaller problems by using Lean Six Sigma tools.
3. Green Belt: Leads small to medium improvement projects and assists Black Belts with larger initiatives.
4. Black Belt: Advanced practitioners who lead complex projects, using statistical tools and methodologies to drive significant process improvements.
5. Master Black Belt: Experts who mentor Black and Green Belts, oversee Lean Six Sigma deployment, and align projects with organizational strategy.
6. Champion: Senior leaders who drive Lean Six Sigma initiatives, ensuring alignment with business goals and providing necessary resources.
Putting Lean Six Sigma into action with ProofHub
Since now you’ve learned all about the powerful strengths of Lean Six Sigma, let’s uncover its practicalities in project management.
While traditional project management practices can derail your Lean Six Sigma efforts, leveraging the right tools can amplify its effectiveness.
And that’s where ProofHub comes in handy – a modern project management solution designed to streamline your Lean Six Sigma practices.
ProofHub’s advanced features and functionalities integrate seamlessly with the DMAIC cycle. Let’s understand how –
Define: With ProofHub’s intuitive task-creation features, defining process improvement tasks becomes effortless. You can delegate tasks, break them down into manageable sub-tasks, and establish dependencies to provide a clear roadmap for team members. Not just that, you can even define the project goals and objectives with precision when outlining descriptions.
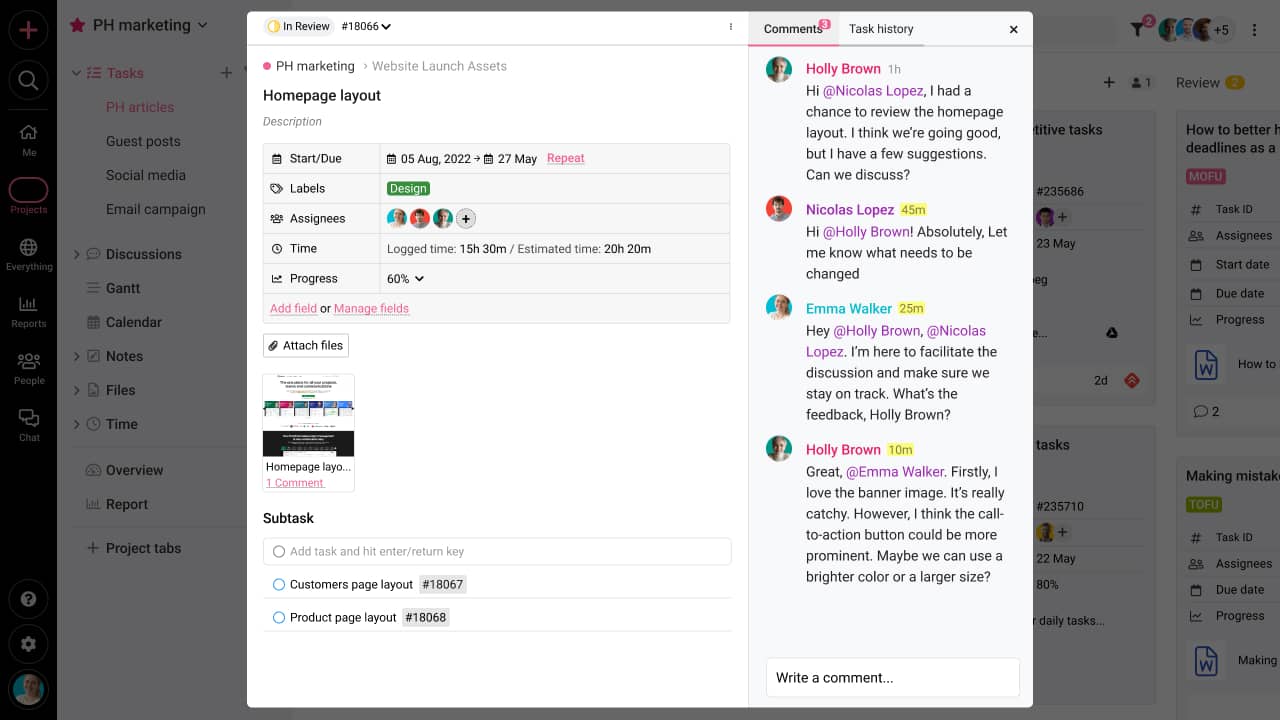
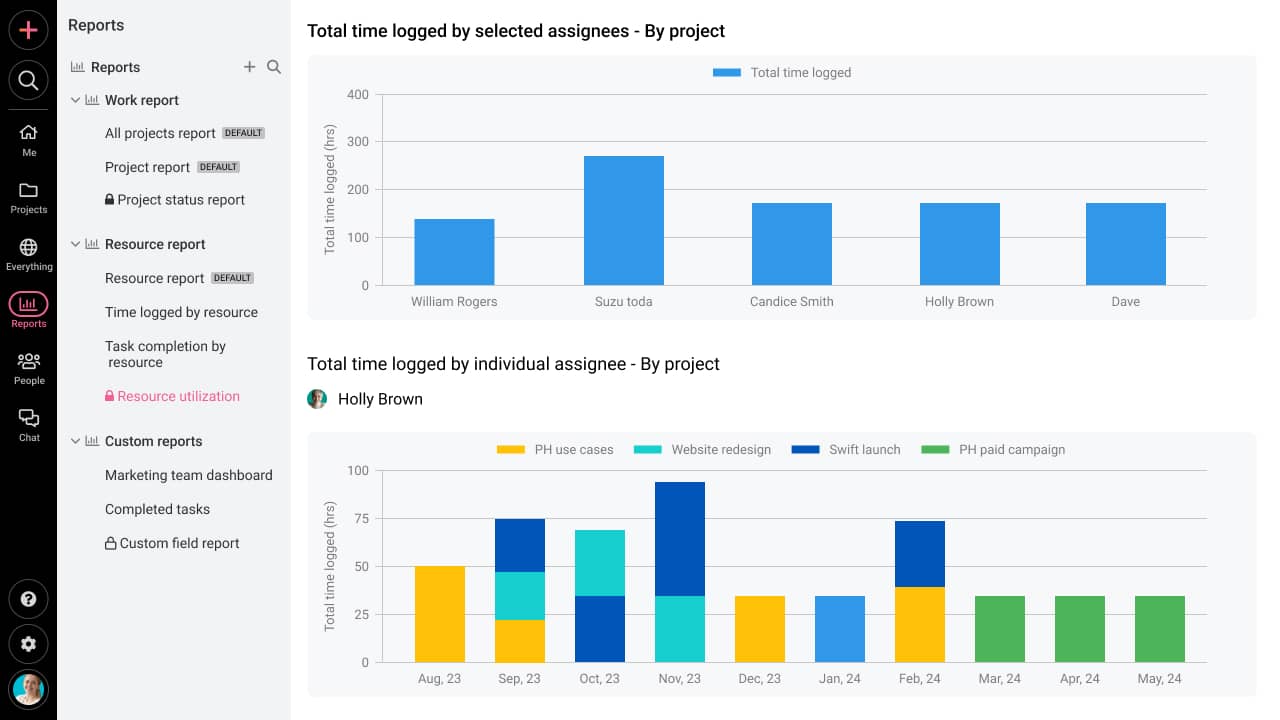
- Measure: ProofHub allows you to analyze data on various project metrics like resource utilization, time logged, task utilization, etc. using reports that can be customized to your preferences. If you want to track how much time your team members spend on tasks, then its time-tracking strengths are also commendable. You can use these metrics as baselines to measure the impact of your initiatives later in the process.
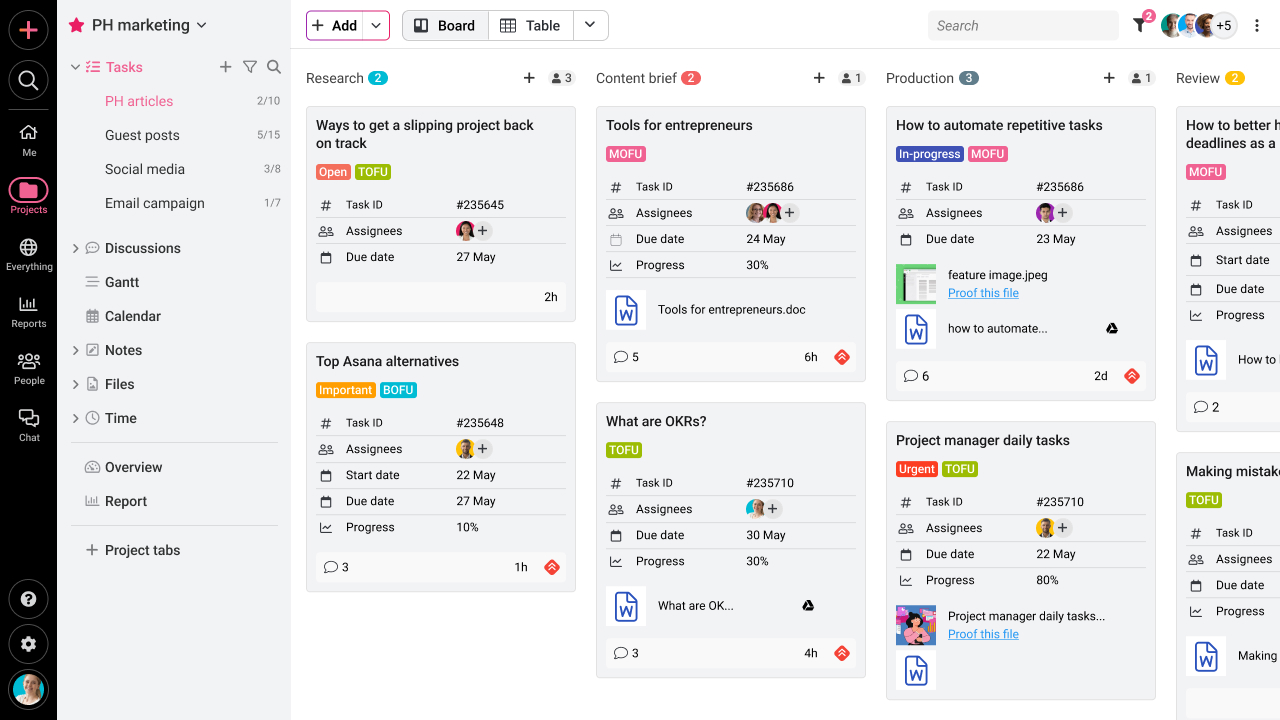
- Analyze: Moving forward, spotting potential roadblocks in your workflow is crucial to prevent frequent delays and rising costs. And that becomes possible with ProofHub’s Kanban boards that provide data visualization of your tasks. You can even look into project timelines to figure out dependencies and optimize schedules using the Gantt chart.
- Improve: ProofHub enables real-time coordination and collaboration among team members to discover optimal solutions for improvements. You can have seamless collaborative discussions, feedback exchanges, and brainstorming sessions with ProofHub’s discussion boards and chat functionalities.
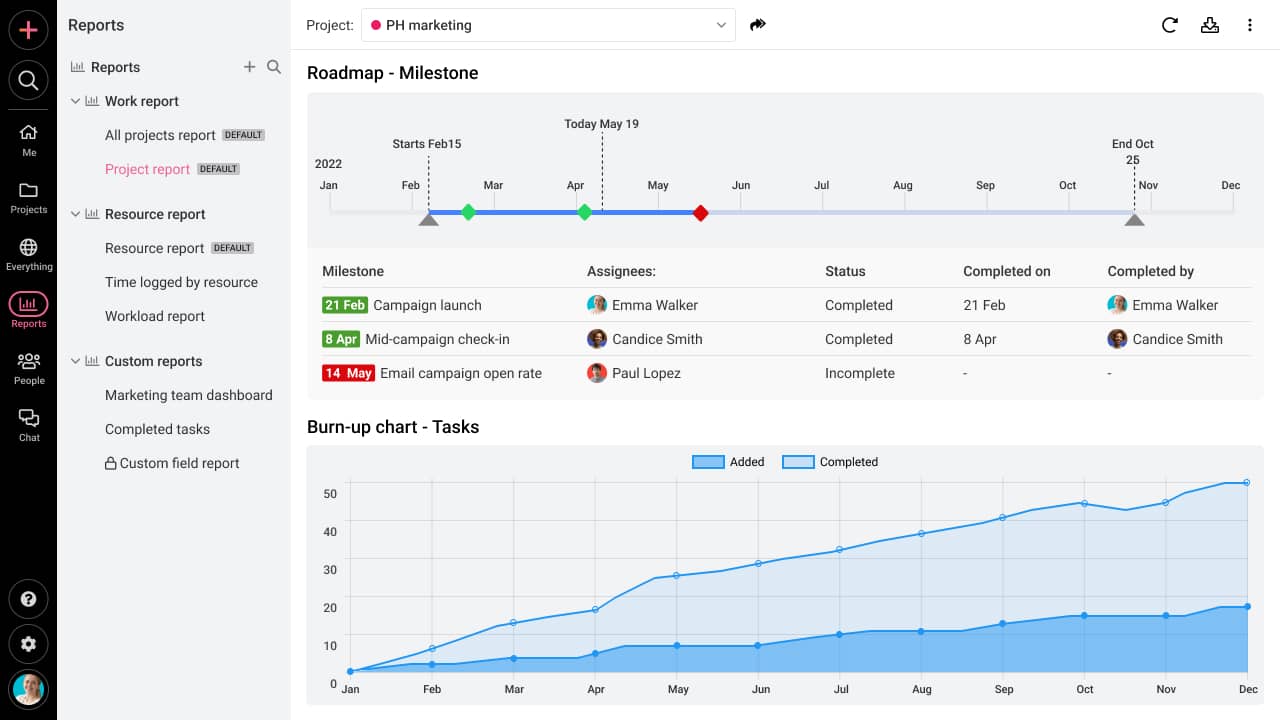
- Control: To stay on top of all the improvements that you made, you can utilize ProofHub’s comprehensive dashboards. These allow you to seamlessly monitor your key metrics and look out for any discrepancies that arise.
ProofHub, alongside supporting Lean Six Sigma practices, empowers project managers and team members alike. It helps you ditch the inefficiencies and make processes more efficient and streamlined.
Conclusion
Lean Six Sigma project management is a powerful blend that offers project professionals and managers some significant benefits. You can start your journey to Lean Six Sigma by exploring online courses, books, and certifications.
You can utilize this methodology in your operations by introducing your project teams to a culture of continuous improvement. A powerful platform like ProofHub is essential to make the process more efficient and streamlined. Give ProofHub a Try for free
FAQs
What role does leadership play in Lean Six Sigma implementation?
Leadership plays a crucial role in Lean Six Sigma implementation. They act as a catalyst for change by bringing a clear perspective to their employees and stakeholders. Also, articulating the organization’s goals and priorities when implementing LSS is a part of their role too.
How does Lean Six Sigma project management differ from traditional project management?
Lean Six Sigma and traditional project management both commit to ensuring on-time project delivery without exceeding budget. However, Lean Six Sigma optimizes existing processes by eliminating waste and reducing defects to achieve quality results.
How long does it typically take to see results from Lean Six Sigma initiatives?
The timeframe for results after Lean Six Sigma initiatives implementation depends on various factors, like, implementation scope, project complexity, team experience, and more. However, a general timeline to witness notable improvements is usually 3 to 18 months. But that is not set in stone.
Is Kaizen Lean or Six Sigma?
Kaizen is neither Lean nor Six Sigma completely. It is closely related to both of these and is a Lean Six Sigma methodology that facilitates rapid improvement in processes.
Is Agile better than Six Sigma for project management?
Choosing one methodology out of the two is difficult. They both bring unique advantages to the project environment. Where Agile focuses on adaptability and building collaboration, Six Sigma prioritizes waste reduction and process improvement.