Introduction
Ever struggled to remember for a client’s name during a presentation, or got blank about the status of the critical report deadline? It happens to the many of us. With so many culprits, such as an overwhelming workload, putting off work, and countless distractions, memory mishaps are bound to happen, making the mastery of effective memorization techniques crucial.
By incorporating powerful memorization techniques into your daily routine, you can transform your memory from unreliable to remarkable, allowing you to retain key details, impress clients, and soar ahead in your career.
How does memorization work?
Memorization happens in two steps, storing information (encoding) and recalling it (retrieval). When encoding information, we use many mental strategies to transform it into a memory, such as connecting ideas, adding details, or forming mental images. By turning on the neuronal connections in the brain, we are able to access these memories later.
There are certain memorization methods which help us to remember things for the long term. Methods like spaced repetition and making connections are helpful for remembering things for a long duration.
On the other hand, techniques like chunking and using mnemonics helps us to recall things more easily in the short term.
What is the process of memorizing?
Human memory measures information retention over time but isn’t a recording device. It is more like a dynamic system whose formation relies on the complex functioning of various brain structures.
Harvard describes the memory working as, “memory operates according to a “dual-process,” where more unconscious, more routine thought processes (known as “System 1”) interact with more conscious, more problem-based thought processes (known as “System 2”).”
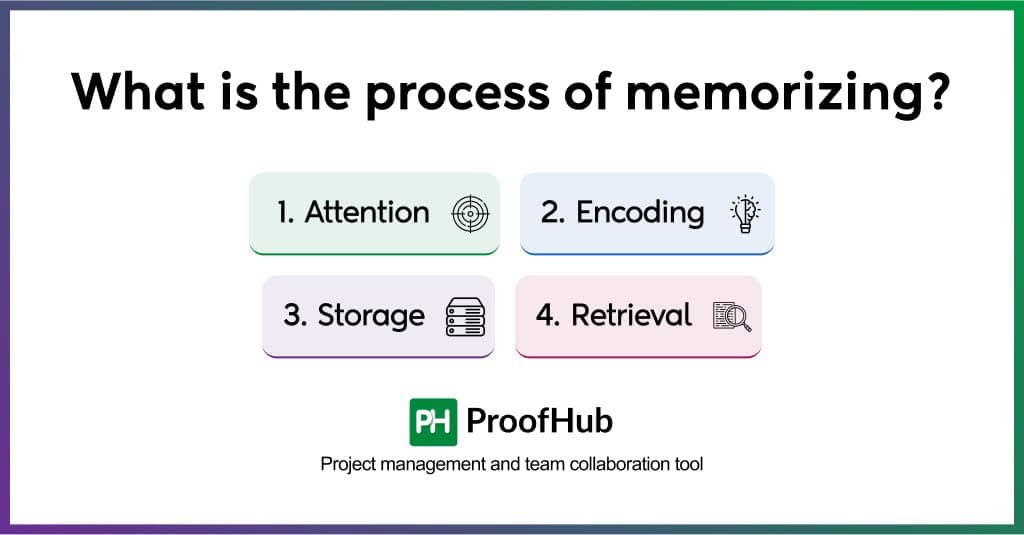
However, when it comes to memorizing information, our brain undergoes a four-step process when exposed to information.
1. Attention
Attention is the first step of the memory process. And our sensory receptors are the prime agents of this process. When you are bombarded with tons of information, these messengers start running to help this information reach your brain.
However, they hold onto this input for seconds until your brain consciously perceives it for your undivided attention. The information only moves to the next stage if your brain discards and filters out this piece.
2. Encoding
In this stage, your brain tries to make sense of the perceived information and encodes it into either short-term/immediate or long-term memory. Information is encoded via either (or more) of these four methods:
- Visual encoding: the way something looks
- Acoustic encoding: the way something sounds
- Semantic encoding: the context or meaning of something
- Tactile encoding: the way something feels
3. Storage
Storage refers to how, how much, where, and for how long the encoded information is stored. Moving any information from short-term memory to longer takes deliberate actions via effective memorization techniques (discussed in the next section). Because if you want information for an unlimited duration, you need to keep up at the right spot for later retrieval.
4. Retrieval
Retrieval is accessing the information stored in our long-term memory when we need it. It is a parameter that describes how well you paid attention, encoded, and stored the information. During memory retrieval, our brain recalls the exact neural activity recorded during encoding. To stay updated with the information, revisit or recall it regularly.
Utilize the power of deep work to exercise your memorization muscles for better retention.
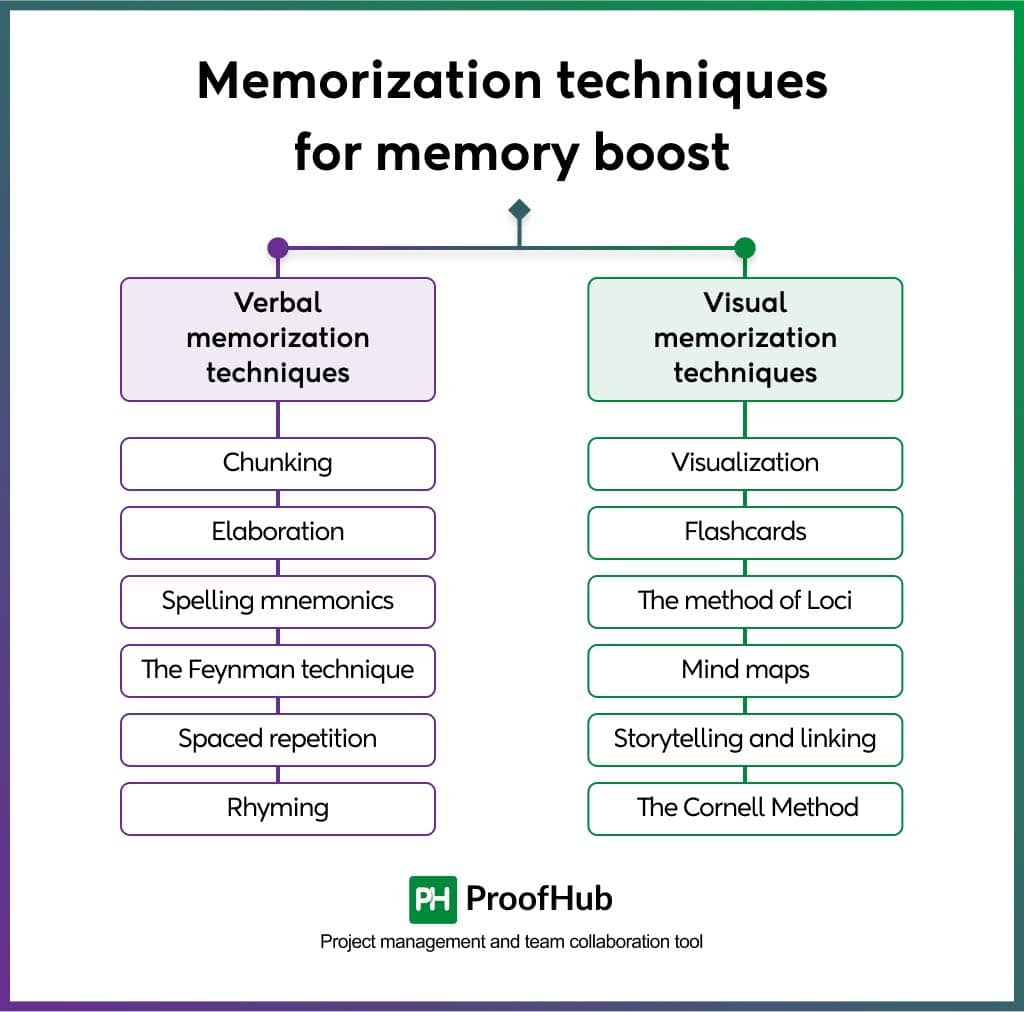
12 best memorization techniques for memory boost
Having better memorization power is a general asset of an individual. However, for working professionals in the business world, it is an invaluable skill to have.
Fortunately, countless memorization techniques can speed up your brain’s processing and improve your capacity to retain information longer.
Verbal memorization techniques
Tired of forgetting names, dates, or key details at work? Verbal memorization techniques can be the solution you are looking for. These strategies leverage the power of words and language to transform fleeting information into long-lasting memories.
1. Chunking
Chunking is the memory technique of breaking down large and complex information into smaller and digestible chunks. This approach removes the overwhelmedness associated with information overload, making it easier to process, understand, and remember the information.
Information recall is easy when broken down into parts: your phone number, grocery list, or technical data. Similarly, in your workplace, suppose you have multiple tasks to handle. You can remember them by project type, deadline, or priority for that matter. Whatever feels right.
2. Elaboration
Elaboration or elaborative encoding links new information to already-known concepts, knowledge, and experiences. By establishing relationships, professionals tend to achieve deeper understanding and remember information for longer.
For example, when learning a new marketing strategy, do not just memorize it. Instead, try linking it to a successful competitor campaign to understand its practical application.
3. Spelling mnemonics
Spelling mnemonics, somewhat similar to chunking, is a great strategy to help you memorize information. Using the first letter of each keyword, you can form an acronym for large information or groups. Some of the examples include-
- KPI – Key Performance Indicators
- SMART – Specific, Measurable, Attainable, Relevant, and Time-based
- SWOT – Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Strengths
- PPM – Project Portfolio management
- WBS – Work Breakdown Structure
4. The Feynman technique
The ideology behind Richard Faynman’s approach is to leverage the power of teaching by demystifying complex information and explaining it to someone else. Especially considering them as laymen ( even if imaginary) with no prior knowledge.
For example, when learning a new software feature, try explaining it to your colleague with no experience with the platform. That way, you will make efforts to solidify and refine your understanding of the concept and identify gaps in it.
5. Spaced repetition
This is a powerful learning technique that builds long-term memory retention by repetition at carefully timed intervals. Spaced repetition helps the brain remember things by reviewing them before you are likely to forget. It is based on the proposition that learning is better over time when spread out.
This involves reviewing material after a certain time, like reviewing after one day, then after three days, a week, and so on. Each time you review it helps you to remember, and it becomes even harder for you to forget.
Spaced repetition is perfect for learning languages, studying for exams, or mastering anything that requires memorization. This way, it saves time repeating things they already know.
6. Rhyming
Rhyming is a fun and easy way to help you remember things better. Our brain remembers patterns and the way words sound when they resemble some kind of rhythm. Converting what you need to memorize into rhymes makes it easier to recall the details. This method works great for remembering lists, steps, or other things that might be hard to remember.
Rhymes help listening and language parts of your brain to remember anything easily. Repetition in rhymes helps the brain to organize quickly and find that information. Whether you make a fun rhyme or match words to a familiar song, it turns boring facts into something you can easily remember.
Benefits of rhyming:
- Better recall: Rhymes are easier to remember than regular information.
- Fun to learn: When one creates rhymes, memorizing becomes a fun challenge.
- Works for everyone: Rhymes are catchy, and so they help with all kinds of memory tasks, such as new words, formulas, or facts for exams.
Visual memorization techniques
Our brains are wired to process visuals exceptionally well. By incorporating these visual memorization techniques into your routine, you can transform complex information into a vibrant mental gallery, boosting your recall and making learning an engaging experience.
7. Visualization
The human mind responds to visual data 60000 times better than text. You can leverage this technology to enhance your memory record by creating mind images using pictures, graphs, charts, diagrams, or scenes. This technique boosts your spatial memory.
Gantt charts are real-time data visualization tools. You can easily measure project progress, set task dependencies, and highlight critical paths to commit them to your memory.
8. Flashcards
By creating flashcards, you can narrow down your focus to essential chunks. You can use different colors and add titles and subtitles to retain the information in your memory. If you do not like creating physical cards, you can even use project management tools like ProofHub to create digital ones.
ProofHub’s stickies are similar to flashcards. You can add quick, actionable items, birthday reminders, links, important phone numbers, and more. You can even choose to change the stickies’ color for easy categorization.
9. The method of Loci (Memory Palace technique)
The University of Pittsburgh defines the method as – “The Memory Palace technique is a memorization strategy, based on visualizations of familiar spatial environments to recall information. “Loci” is the Latin term which means “places” or “locations”.”
These places could be anything you are already familiar with: your office building, break room, desk, meeting room, elevator, or something else.
For example, you can assign a visual cue to each section in your office while preparing for a presentation. You can even sequence the locations for better recall and revisit these to trigger your memory.
10. Mind maps
This is a great memorization technique that help you to remember things visually. Mind maps allow you to create a visual representation of ideas rather than creating a list or paragraph. This makes your brain connect with different pieces of information and recall them.
A mind map starts with a topic and then branches out into related ideas or details. Each branch is connected to the main idea and splits into more branches for further details. This is similar to how your brain organizes information, making it easier to remember.
Using mind maps technique to organize and connect ideas makes learning more effective and enjoyable and helps you to remember things for a longer time.
11. Storytelling and linking
Storytelling and linking are powerful techniques that help you remember things by linking them to a story or connecting them to something you already know. This makes learning easier and easy to recall.
When you connect the information with a story, your brain finds it easier to recall the details. Linking connects information to something familiar, making it easier to remember because you are relating it to something you already know.
12. The Cornell Method
If you are someone who loves to write things down, then this technique is best for you. When we write down important pieces of information, it encourages its active processing in the brain. You can even refer back to them anytime.
With ProofHub’s notes, you can capture everything visually and boost your memory. You can keep it for your personal use or even add additional subscribers for collaboration. The color code option facilitates better organization and segmentation.
Tips for memory improvement
While no doubt the above methods yield powerful results, here are some additional tips to keep your brain healthier and agile:

1. Get enough sleep and exercise
Sleep improves the ability to recall complex events. During sleep, your brain consolidates all the events and memories. Sleeping 7-8 hours each night is essential to optimizing memory functions. A sleep-deprived individual impairs an individual’s ability to concentrate.
2. Limit alcohol and caffeine
Excess alcohol consumption disrupts the brain’s function and interferes with the memory formation process. So, be mindful of your alcohol intake practices. Also, caffeine affects sleep quality, especially when consumed in the afternoon and evening.
3. Eat a healthy diet
A study finds, “A balanced diet was associated with better mental health, superior cognitive functions and even higher amounts of grey matter in the brain — linked to intelligence — compared with those with a less varied diet.”
What you consume greatly impacts your ability to think and memorize. Consuming healthy foods like milk, cheese, fish, and eggs and avoiding natural sugar, refined sugar, and saturated fats promote long-term memory functions.
4. Manage stress
Jill Goldstein, a professor of psychiatry and medicine at Harvard Medical School, says, “Stress affects not only memory and many other brain functions, like mood and anxiety but also promotes inflammation, which adversely affects heart health.”
So, to deal with stress, engage in stress reduction techniques like yoga, meditation, cardio, or deep breathing exercises. It helps you improve concentration and focus in your routine life.
5. Actively recalling information
Don’t be passive in your approach to consuming information. By this, I mean actively engaging when understanding a concept. This will strengthen your memory pathways and enhance retention.
ProofHub: A valuable tool for enhancing memory and information retention
Since you now know all the effective ways to remember things, do not underestimate the contributions memorization tools can make to improving your memory.
ProofHub, with its comprehensive and robust features, creates an environment for you to support your memory. It supercharges your memory improvement journey.
Let’s find out how ProofHub empowers memory improvement at work:
- Centralized knowledge base: ProofHub creates a central knowledge base for all your assets, such as documents, notes, files, meeting agendas, etc. You can return to its interface for quick reference and retrieve necessary information. This results in reduced cognitive load and improved recall.
- Task management: With its transparent approach to task management and deadlines, ProofHub presents a clear work picture to everyone. It helps reduce mental clutter and frees up working memory space to memorize important details.
- Discussion boards: Discussion plays a major role in deepening understanding and knowledge in a working environment. When team members share experiences, ask questions, and hold each other accountable, concepts are better understood and memorized.
- Task reminders: Setting up task reminders helps users stay updated with the current workflow. This ensures they never miss any crucial information, improving focus and memory.
- Visual aids: ProofHub’s visually pleasing interface appeals to visual learners. Its colorful yet intuitive visual tools, such as charts and diagrams, enhance memorization.
- Workload management: ProofHub minimizes cognitive strain and individual workload by managing workloads. This expands your mental bandwidth, allowing you to remember everything with less effort.
Related articles
- Discover 13 effective strategies to stay focused at work and memorize things for longer
- 17 Best morning routine ideas for a productive day
- 12 Time management tips for work to achieve more
- 22 Effective time management strategies for work
- 10 Effective ways to stay organized at work
FAQs
Can memorization techniques help with remembering names and faces?
Yes. Memorization techniques like association, visualization, and contextual cues are some of the effective techniques for helping with remembering names and faces.
What foods are good for memory?
Almonds, walnuts, green leafy vegetables, berries, dark chocolate, and seeds are some memory-boosting food items.
How do you improve concentration and focus while using memorization techniques?
Avoid multitasking to improve concentration and focus while using memorization techniques. Multitasking hinders focus and divides attention.

