We’ve all been there.
You meticulously plan a project, feeling confident in your timeline and resource allocation. But then, an unexpected hurdle throws everything off track.
The culprit? Often, it’s hidden project assumptions that snuck into your plan unnoticed.
This guide empowers you to take control. It will equip you to uncover hidden assumptions, assess their impact on your project, and develop strategies to manage them.
Let’s turn assumptions of a project from silent threats into predictable elements of your plan, ensuring success from the start.
A Free guide to help you with proven ways to lead a project from start to finish, without confusion or jargon.

What are project assumptions in project management?
In project management, assumptions are factors believed to be true or real, even without any real evidence. These assumptions vary from each phase of the project lifecycle.
A project manager has to make certain assumptions related to the market, resources, technology, scope, or some other project factors. If they do not, it is hard to proceed ahead because there is simply no way to give proof or certainty for everything in a project plan.
Here are a few examples of project assumptions that can include different aspects:
- You assume that your team will deliver the project on time,
- You assume that you will be done with this project within the cost,
- You assume that your skilled team member will handle the project alone,
- You assume that the price of the tools related to the project remains the same,
- You assume that nature will not interrupt your project’s progress,
Importance of project assumptions
A research paper published in the International Journal of Project Organisation and Management says, “Project assumptions are fundamental aspects on which the decision to start a project is based. If project assumptions are about to become invalid, it is an important early warning signal to projects.”
It’s essential to check and verify project assumptions as the project progresses regularly. Incorrect assumptions can disrupt the project’s progress.
For instance, if a key team member takes leave, you may need to adjust timelines and reassign tasks to ensure the project stays on track.
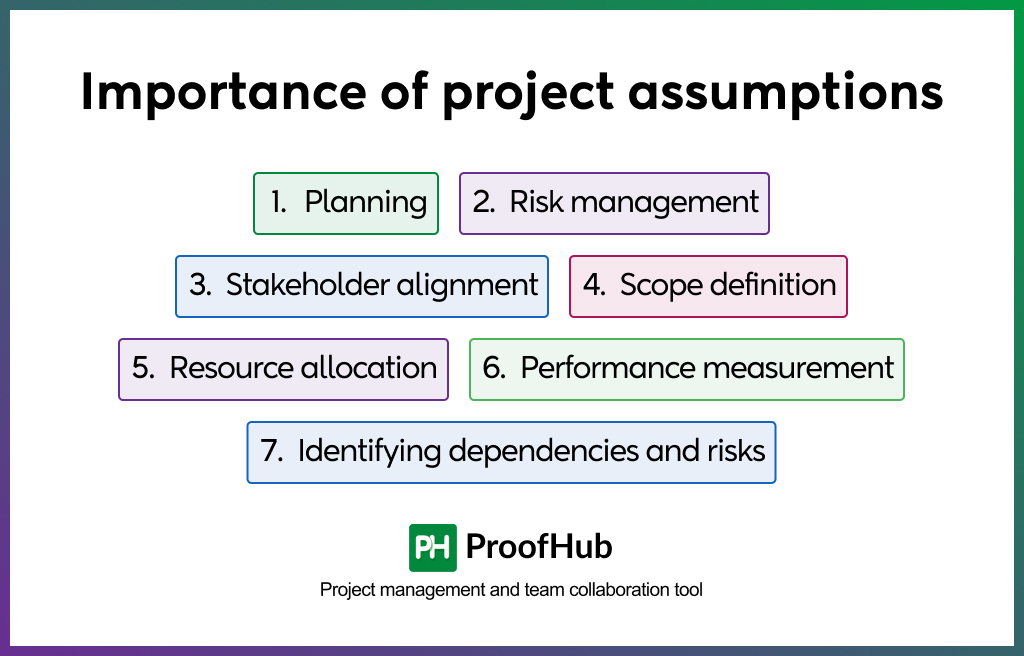
Project management assumptions are important for the following reasons:
- Planning: Assumptions are the foundation for planning and decision-making.
- Risk management: Assumptions are essential for developing a risk management plan.
- Stakeholder alignment: Assumptions help with stakeholder alignment.
- Scope definition: Assumptions help define the project’s scope.
- Resource allocation: Assumptions help with resource allocation.
- Performance measurement: Assumptions help measure project performance.
- Identifying dependencies and risks: Assumptions can help identify dependencies and risks, such as the number of resources required for a project.
Adding to the above, the purpose of making project assumptions is to open the door for project initiation and provide you with a better understanding of whether the project’s goals and activities are realistic and achievable in the given timeframe.
You need to manage the assumptions of a project to ensure that if any assumption is false, its impact on project outcomes will be minimal.
Read more: 11 Best project planning tools for project management in 2025
The difference between project assumptions, dependencies, risks, and constraints
People are often confused between these four elements. So, Understanding the difference between project assumptions, constraints, dependencies, and risks is very important for effective project management. Each element plays a different role in planning and executing the project. Here is a quick overview:
Project assumptions
Project assumptions are the factors considered true or certain for project planning purposes, but they are not verified. These assumptions help to fill the gap between information and guide the project’s direction.
For example, assuming every team member will be available on specific dates and complete the project within a specific timeframe are common project assumptions.
Project constraints
Project constraints are the limitations related to the project’s budget, scope, schedule, quality, resources, and risk. Team members have to work within these limitations and a project manager might not have control over the project constraints.
For example, you may have a certain budget and timeframe for a project. A cost constraint means you have to complete the project within the specific budget and a time constraint means you need to complete the project within the specific schedule.
Project risk
A project risk is a potential event that might occur in the future and has the power to impact the project’s outcome, schedule, projected costs, and overall success.
For example, A skilled team member might be unavailable when needed.
Project dependencies
Project dependencies refer to activities and tasks that directly depend on the completion of another activity or task. They help maintain project schedules and ensure smooth teamwork.
For example, A developer cannot begin coding a feature (Task B) until the requirements document is finalized (Task A).
Types of project assumptions with examples
Project assumptions are related to the project’s scope, resources, cost, time, quality, and other factors associated with the project.
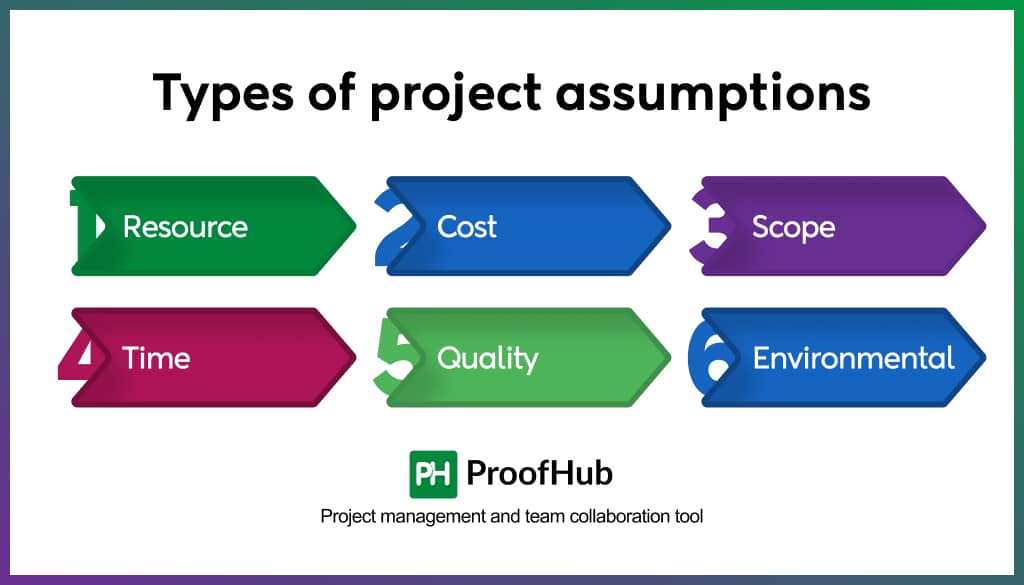
Project assumptions are primarily of six types:
1. Resource
Resource assumptions cover the assumptions related to the project resources; both tangible and intangible.
For example:
- All of the project team members will be available to fulfill their project roles and responsibilities.
- All of the required equipment and technology will be in good working condition and available for use throughout the project.
- Project team members will have the skills required to work on a project and resolve the conflicts
2. Cost
Cost assumptions assume that the projected costs of the resources utilized in a project will not change.
For example:
- The cost of human resources will not exceed the budget allocated for the project.
- Material, equipment, and technology costs will remain stable throughout the project or not exceed the estimated cost.
- Market dynamics such as inflation will rise as expected.
3. Scope
Scope assumptions talk about the assumptions related to the scope of the project.
For example:
- A project manager assumes a project’s requirements, milestones, deliverables, and boundaries will not change throughout the project lifecycle.
- Clients and stakeholders will not request any changes to the project once it is delivered.
4. Time
Time assumptions believe there will be no change to a project’s schedule, duration, and sequencing of activities.
For example:
- Holidays and team leaves are accounted for and will not impact the project timeline.
- A manager assumes tasks will be completed within the planned time frame, task dependencies will be followed, and there will be no significant delays in predecessor activities.
5. Quality
Quality assumptions make assumptions related to the quality of the work.
For example:
- A manager assumes the project team members will follow the established quality assurance guidelines and work on the project deliverables as specified in the acceptance criteria throughout the project lifecycle.
- Clients and stakeholders will provide timely feedback to ensure the quality of the project is maintained.
6. Environmental
Environmental assumptions talk about the assumptions related to the external factors of a project. These include social, economic, political, legal, and natural factors that can influence the project’s outcomes.
For example:
- The laws, policies, and regulatory environment will remain the same and not undergo significant changes that could impact the project’s compliance requirements.
The quirkiest thing about the project assumptions is that they can be true or false. That’s where you need to manage project assumptions. If you do not, it will convert into project risks and impact the project outcomes, scope, budget, quality, and time, or even lead to overall project failure.
I have recently run a poll on LinkedIn on project assumptions. Here is what I found:

Read more: Reasons for cost estimation inaccuracies in project management and how to avoid them
How to write project assumptions?
A project manager needs to create a project assumption log to document all the project assumptions. It acts as a key piece of document to identify, document, track, and manage all of the project assumptions. It is included in other key project documents, such as project charter, business case, and project scope, to create a project plan.
You need to learn to create a project assumption log to write project assumptions. Have a look at the project assumption log template and best practices for writing project assumptions that can help you write project assumptions.
Project assumption log template
Certain elements need to be present in the project assumption log. Have a look at them to understand how to create a project assumption log template.
- Name and description: Enter the name and a brief description of an assumption
- Identity number: Assign a task ID to each assumption
- Category: Define the category of the assumption, such as resource, cost, scope, or time
- Logged date: Enter the date assumption is first logged
- Impact: Describe the impact and mention the impact rating for the assumption whether it is high, medium, or low
- Likelihood: Mention the likelihood of the assumption to happen, such as high, medium, or low
- Owner: Assign the owner for the assumption who is responsible to validate the assumption
- Action Plan: Define the action plan to mitigate the impact of the assumption
- Status: Enter the status of the assumption, whether it is closed or opened
- Validation date: Enter the date of validation
- Comments: Add in any remarks in this section
A project assumption log is created during the initiation phase of the project. However, it should be regularly reviewed and revised throughout the project lifecycle to accommodate changes.
You can also use a RAID template to document risk and a RACI matrix for risk management.
Best practices for writing project assumptions
Project assumption forms the basis of project plans and risk management. It is referred from time to time by project team members, stakeholders, and a project manager to make key decisions related to the project. That’s why it is important to write clear and well-defined project assumptions.
Here are the five best practices for writing project assumptions:

1. Write a clear description and define its impact
A project assumption should be clear and specific. It should not confuse the reader or make an ambiguous statement. After writing the description, define its impact on the project. Be specific, do not use vague language, and keep it related to the project.
2. Frame assumptions as a statement
The best way to frame a project assumption is as a statement. It should describe what you expect from a project factor.
3. Follow the format specified in the assumption log
Certain details are associated with a project assumption such as name, category, logged date, owner, and status. Add all the details of the assumption specified in the assumption log.
4. Involve stakeholders and team members to capture assumptions
A project manager can identify and validate all the project assumptions. Meet with stakeholders and brainstorm with team members to identify key assumptions for a project.
5. Validate assumptions
Validating an assumption is crucial. Assign assumption validation to the subject matter experts of the assumption. Update the assumption as required.
What is assumption analysis in project management?
Assumption analysis in project management is the process of identifying, documenting, and validating project assumptions. The purpose of assumption analysis is to minimize the risks involved in making assumptions.
Here is what this technique includes:
- Project team members, subject matter experts, and key stakeholders identify the project assumptions and document them in a list.
- Documenting a project assumption includes mentioning the details of an assumption, the rationale behind it, and its impact.
- Then one by one, validation owners analyze the assumption from the polarized perspective of validity and falsehood. It means finding out whether an assumption is valid or false, estimating the impact of the valid assumption if it proves to be false later, and creating an action plan to mitigate the project risks.
According to the A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide), “Assumptions analysis is a very effective planning tool that is inferred to be applied within many of the PMBOK® Guide processes, yet it appears only once within its tools and techniques category. It is found in the Identify Risks process, a process in the Project Risk Management Knowledge Area.”
Read more: Project management framework – A comprehensive guide you must read
Mistakes to avoid when making project assumptions
Making project assumptions seems like a simple task, but it is not uncommon to make mistakes.
For example, one of the principles of Strategic Assumptions Surfacing and Testing says, “The best way to test an assumption is to oppose it.”
However, in many cases, project managers do not question the validity of the assumption. Thus, when an assumption turns out to be false, they do not have a plan to mitigate the impact.
Therefore, it is necessary to avoid such mistakes when making project assumptions.
Here are the top five mistakes to avoid when making assumptions:

- Making assumptions in silos: No doubt as an experienced project manager, your opinion matters the most. But making project assumptions individually in silos will refrain you from capturing the different perspectives. Involve stakeholders and team members in gathering and validating project assumptions. You can use stakeholder mapping to identify all the stakeholders who can help you find project assumptions.
- Not validating the assumption: Accepting the assumption without the analysis of whether it is true or false is the biggest mistake. It leads to poor risk management and mitigation.
- Not documenting assumptions: All project assumptions and their details need to be documented. Use the project assumption log to document the assumptions. Not documenting the project assumptions leads to gaps in risk management during the project execution.
- Not reviewing the assumptions: Project assumptions change as the project progresses. Not reviewing the project assumption leads to inaccurate estimates of risks. Thus, you need to revisit the project assumption log from time to time.
- Not tracking and updating the assumptions: For most individuals, once a project assumption log is created, they forget it. However, the high-impact project assumptions need to be tracked every day and their mitigation plan should be updated as you gather knowledge about the project progress.
Manage project assumptions in real-time with ProofHub
Project assumptions have a direct impact on the project plan and the project’s risk management. The better you make and manage assumptions, the better the chances of successfully planning and managing a project’s risks.
That’s where ProofHub comes into play. It makes identifying, documenting, and managing project assumptions easy to ensure the project’s success.
1. Identify all the project assumptions
First of all, you have to identify all the project assumptions. Conduct brainstorming sessions with your project team members and meetings with stakeholders. It will help you identify and agree on project assumptions.
Apart from that, you can use your experience as a project manager to make an educated guess of some project assumptions.
Other sources of identifying project assumptions are similar past projects, industry standards, and market statistics. These will help you create a list of things that you will assume to happen or not.
2. Document the project assumption
The project assumption log is the most important document for managing project assumptions. It lists details of all your project assumptions and is accessed by all team members who are involved in working on a project.
Document all the assumptions in the project assumption log, assign a unique ID number to each assumption, and add the assumption description.
3. Validate assumptions
Not all project assumptions you make are valid. Some are valid and going to happen and you have to plan for it, while others are not valid and you have to plan some other course of action for it.
Utilize the expertise of stakeholders, subject matter experts, and experienced employees to validate the project assumptions and make a final list of the project assumptions.
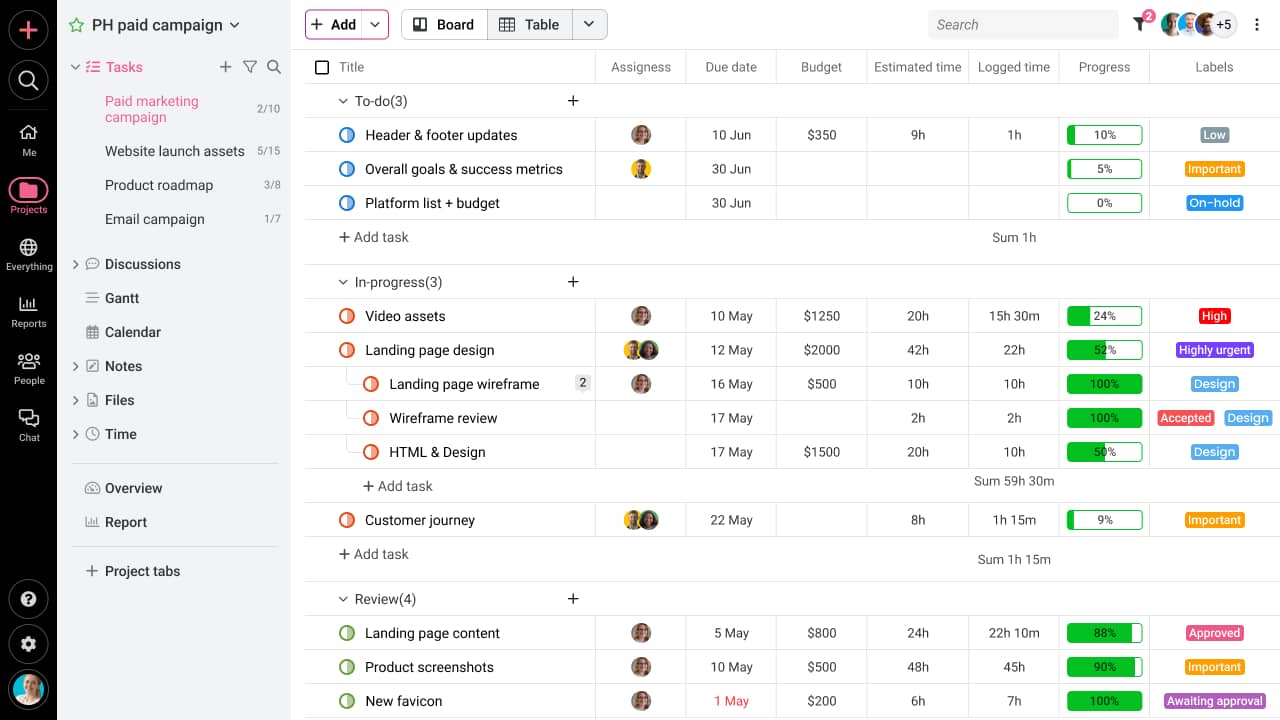
4. Prioritize assumptions
Just like project risks, you have to prioritize project assumptions. This is because not all project assumptions have equal impact and probability of being proven false. Assign the impact of each assumption and determine its likelihood to be proven false. You can use the impact and likelihood matrix to prioritize your assumptions.
5. Manage project assumptions
Once you have created the list of all the project assumptions, you have to create a mitigation plan for each project assumption. The thing with project assumption management is that it is not a one-time process.
You need to regularly visit your project assumption list, change the status of the project assumption, and add new project assumptions. You have to pay particular attention to high-risk, high-impact assumptions, validate their accuracy, and adjust plans and actions accordingly.
Frequently asked questions
Why are assumptions harder to manage?
Assumptions are built on the basis of the educated guess derived from the beliefs, knowledge, and past data collected over the years. When assumptions are not validated and verified, they become harder to manage.
Why can assumptions be damaging?
Assumptions can be damaging because there is no proof for an assumption to be real, true, or certain. Every assumption poses a risk, but at the same time, we cannot proceed ahead with a project without making project assumptions.
How do you avoid wrong assumptions?
The best way to avoid wrong assumptions is to use the assumption analysis to validate the project assumptions. It includes reviewing the assumption for the validity and falsehood and analyzing its impact.
How can incorrect assumptions affect decision-making?
Incorrect assumptions lead to inaccurate estimates of project scope, cost, time, resource, quality, and risks. Thus, when you have made the wrong estimates and assumptions, it is hard to avoid the project failure.
Why are assumptions bad for business?
Assumptions are bad for business because each assumption poses a risk. However, how dire risk an assumption poses depends on the impact and likelihood of the assumption.
Read more:

