Cost is a key project factor that matters most to the business owners.
It is because they want to make profits from the business.
However, more than 40% of the projects suffer from cost overruns.
Thus, it is very important to manage project costs to avoid cost overruns proactively.
Project cost management is the key here. It focuses on maintaining the financial control of a project to ensure it is completed within budget.
In this post, we will learn about project cost management, its importance, and its benefits. We will talk about the four processes of project cost management, cost estimation techniques, and how to create a project cost management plan.
What is project cost management?
Project cost management is the process of planning, estimating, budgeting, and controlling the cost of a project. The purpose of project cost management is to manage project costs to improve a business’s net earnings from a project.
The project cost is not an independent factor. It is one of three constraints of the traditional project management triangle (cost, time, and scope) that is directly influenced by the project’s scope and time. It means changes in the project’s scope and time can lead to changes in the project cost.
A Free guide to help you with proven ways to lead a project from start to finish, without confusion or jargon.

Types of project costs
To make accurate cost estimates, it is important to know all types of project costs. Project costs are explained in five types:
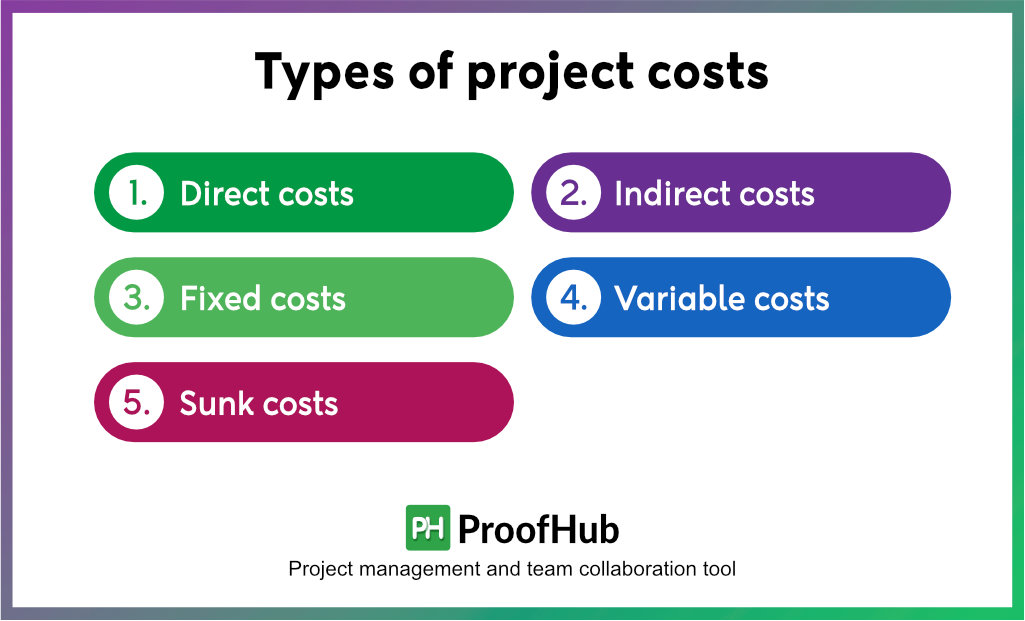
- Direct costs: These are the project costs directly related to project activities and are easy to identify. For example, salaries of project team members, materials used to build a product, technology cost, and costs of renting equipment specific to the project.
- Indirect costs: These are the project costs that are not directly related or attributed to the project. It includes costs like administrative costs, utilities, and insurance.
- Fixed costs: These are the project costs that remain fixed throughout the project lifecycle. For example, salaries of the permanent resources assigned to the project, software license fees, rental fees for office space
- Variable costs: These are the project costs that vary or occur due to changes in the project scope or timeline. For example, overtime pay, fuel cost, labor hourly charges
- Sunk costs: These are costs that have already been incurred and cannot be recovered. It should not be considered when making future project decisions. For example, marketing research and feasibility study costs.
Importance of project cost management
As per the PMI, “The first step of the project cost management is to determine whether a project is economically and technically feasible and whether sufficient funding can be obtained to implement the project.”
This first step alone indicates the importance of project cost management. Without project cost management, an organization can easily commit to a project that is economically not feasible. It can even derail the organization; not just a project.
The Denver International Airport’s automated baggage handling system project is the most popular example of poor project cost planning and management. The original budget of the project was $193 million, but the final cost ended up being over $1 billion. The project was never fully completed due to the massive budget shortfall.
This failure might not have happened if effective project cost management had been in place.
Project cost management offers many benefits to an organization. Have a look at them.

1. Plan a project costs better
Project cost management involves defining the detailed scope of the project. This allows you to identify and predict costs better for each task. This helps you secure a realistic budget for the project.
2. Keep the project costs under control
When you have a project budget, it acts as a cost baseline for the project expenses. A project manager has a clear idea of how much money they have to spend. Based on that, they make decisions and keep the cost under control.
3. Make sure resources are utilized efficiently
With everything outlined in a project cost management plan including human resources costs, a project manager uses resources efficiently. It is because delays in a project’s progress mean the extra time required to complete the job, leading to increased project costs.
4. Handle the project risks better
Without an effective cost tracking and control system, it is easy to overrun the project costs. If your actual projects are deviating from the planned costs, you can identify the cost variances and take action to get costs back on track. This helps you plan the project cost risks better.
5. Manage scope creep better
In some industries such as IT, there are high chances that a client keeps adding new features. An increase in scope means you need more time and resources, leading to an increase in project costs. It provides a framework for re-estimation of the project costs based on the new scope.
Project cost management processes
Project cost management is a process that includes four phases: Resource/Cost planning, Cost estimation, Cost budgeting, and Cost control.
Here is the description of each phase of project cost management:

1. Cost planning
Cost planning is the first step of the project cost management. It includes defining the resource requirements to complete each task of a project. The resources include human resources, materials, equipment, and technology.
To do so, a project manager defines the scope of the project because without knowing what you need to work on, it is hard to predict resource requirements for a project and make cost estimates.
A project manager breaks the project into detailed tasks using a work breakdown structure. Then, the resource requirements for each task are identified. This will give you a fair idea about the work that needs to be completed in a project and help predict resource requirements to complete those tasks.
2. Cost estimation
Cost estimation is the process of estimating the costs of the resources you outlined in the resource plan. including assigning costs to each specific resource. This step is vital in project cost management, as the accuracy of your cost estimates directly influences the accuracy of your overall project budget.
In the most basic form, cost estimation can look something like this:
- Resource requirements for a task
- Price of each resource
- The duration of each resource is required
Companies use a set of cost estimation techniques, methods, and practices to make accurate cost estimates.
3. Cost budgeting
Cost budgeting is the process of summing up all the costs of a project. It includes combining all types of project costs, such as direct, indirect, fixed, variable, and additional costs, such as contingency reserves for risk management.
The purpose of cost budgeting is to create a project budget that acts as a cost baseline. It acts as a cost reference for a project around which all the comparisons of actual costs to the planned costs will be made throughout the project lifecycle.
4. Cost controlling
Cost control is the process of tracking and controlling the costs of a project. It includes regularly performing activities to identify cost variance from the original plan and procedures to get costs back to the cost plan. If cost discrepancies vary too much from the budgeted cost, you need to inform the stakeholders of that.
How to calculate the cost of a project?
Project cost estimation techniques are used to estimate the cost of the project. Here are the top techniques used for project cost estimation:
1. Analogous estimating
Analogous estimating is a cost estimation method that uses historical data from previous projects for similar tasks to make cost estimates for new projects. It is an ideal method for projects that do not have information available on the scope.
The accuracy of the method depends on the amount of historical data available for previous projects and the similarity of the new project to previous projects.
It is a top-down project cost estimation method where you make an estimate of the project cost first and then break it into smaller elements.
2. Bottom-up estimating
Bottom-up estimating is the cost estimation method that calculates the cost of individual tasks of a project at a minute level and adds up the costs of all the tasks to create an estimation of the overall cost of the project. It is an ideal method for projects that have information available.
It is the most accurate method of cost estimation as it is granular and evaluates all the components of a project.
3. Parametric estimating
Parametric estimating is a cost estimation method that combines historical and statistical data to make cost estimates. It uses mathematical formulas that take the historical value of the parameter from an old project and take into account the current value of the parameter in the new project to make cost estimates. It strikes a balance between analogous and bottom-up estimation methods.
4. Three-point estimates
Three-point estimates is a cost estimation method that develops three scenarios for a task to make cost estimations: most likely, optimistic, and pessimistic ranges.
- Most likely (M) estimate: It represents the most likely scenario and predicts the cost of the task based on that. As per the PMI, the most likely (M)/best guess (BG) is the average amount of work the task might take if the team member performed it 100 times.
- Pessimistic (P) estimate: It represents the worst-case scenario and predicts the cost of the task based on that. The amount of work the task might take if the negative factors they identified do occur.
- Optimistic (O) estimate: It represents the best-case scenarios and predicts the cost of the task based on that.
The two most common types of three-point estimating formulas are the triangular distribution and the Beta distribution (PERT).
5. Reserve analysis
Reserve analysis is a cost estimation method that calculates the contingency fund reserved to manage project risks. The amount of the fund reserved is directly proportional to the project risks.
These five cost estimation techniques can help you make accurate estimates of project costs.
Project cost estimation example
Let’s understand project cost management from a simple example of an e-commerce website development.
Project: A company wants to build an e-commerce website.
1. Resource requirements
A project manager identified resource requirements.
- Developers, designers, and content creators.
- Software licensing costs for design tools and content management systems
- Third-party integrations
2. Cost estimation
Using historical data and industry benchmarks, a project manager estimated hourly rates for each resource and defined software licensing costs.
- Developer cost: $30 per hour x 40 hours = $1200
- Content creator cost: $15 per hour x 20 hours = $300
- Designer: $20 per hour x 15 hours = $300
- Domain cost: $10 per year
- Shared hosting cost: $60 per year
- Third-party integrations:
- Premium theme: $80
- Premium plugins: $30 per year
- A website builder: $15 per month for a basic plan ($180 per year)
- Payment gateway: $30 per month ($360 per year)
- Google Analytics and other tools: $40 per month ($480 per year)
The estimated cost of a website development project is $3000.
The cost of human resources is calculated using the hourly rate. Depending on the project, you can calculate the project costs using a flat rate or cost-plus pricing method.
3. Project budget
The project team created a detailed project budget by summing up all the estimated costs and adding contingency reserves.
Contingency reserve: $500 (Usually it is 10% of the project budget for large projects)
The project budget for e-commerce website development is $3500.
- Phase 1: $1500
- Phase 2: $1000
- Phase 3: $1000
4. Cost control
A project manager implements cost control measures throughout the project lifecycle, such as:
- Monitoring actual hours worked by developers and designers against estimated hours
- Comparing actual expenses to the budget and identifying any variances
Some key variances:
- Developers worked 10% more hours than estimated
- Hosting costs were 20% higher due to more data
- Additional 3rd party integration required
The project manager addresses cost variances by identifying cost savings in other project areas and using contingency funds.
How to create a project cost management plan?
A project cost management plan is a key document that outlines how you are going to manage project cost management activities: cost planning, budget execution, cost tracking, and cost controlling. This enables project managers to estimate costs for the tasks easily, allocate resources accordingly, and control overall spending.
The key elements to include in a cost management plan are:
- Work breakdown structure
- Cost Baseline
- Cost control threshold
- Precision levels
- Measurement units
- Performance measurement
- Reporting
Steps to create a project cost management plan
A project cost management plan guides how to estimate, budget, track, and control project expenses throughout the project lifecycle.
Here is a step-by-step guide to creating a project cost management plan:
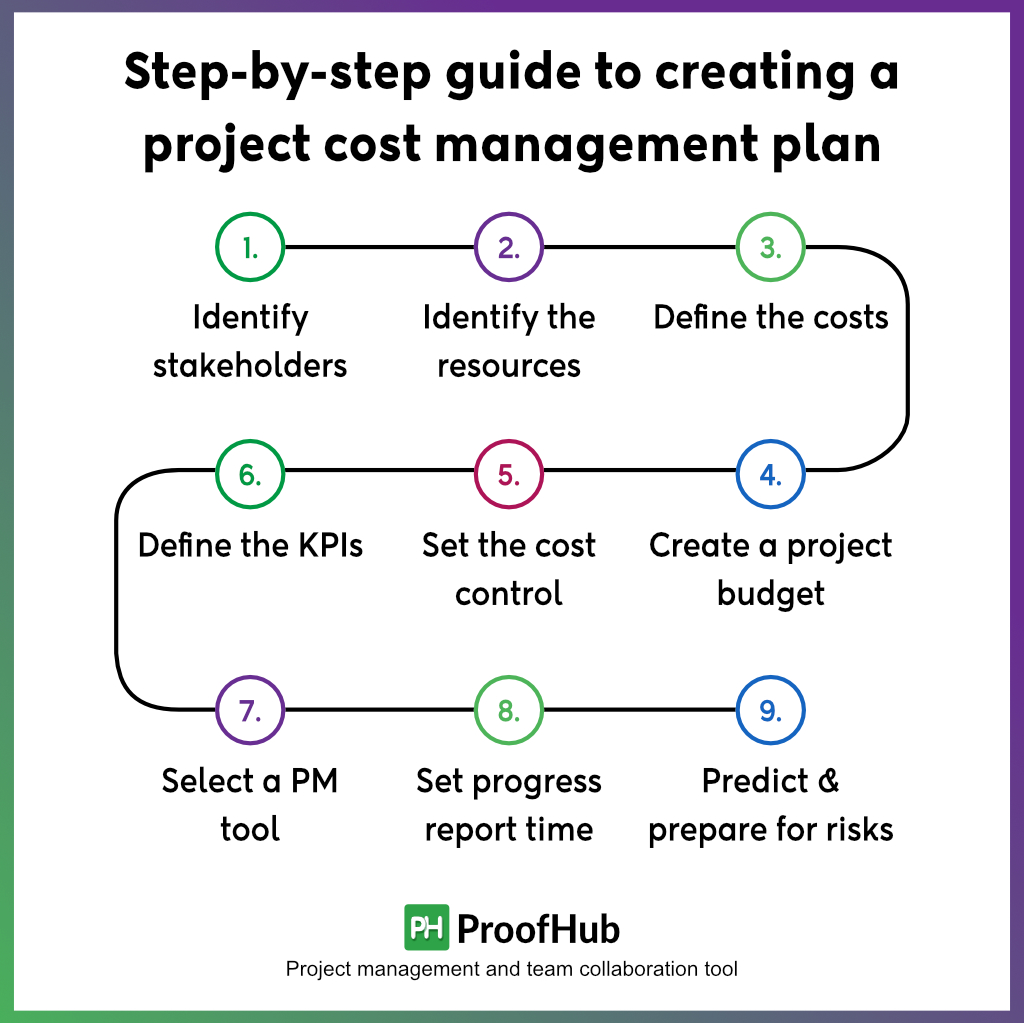
Step 1. Identify stakeholders who will be impacted by the project and involve key stakeholders in the planning process.
Step 2. Identify the resources required for the project, build a work breakdown structure, and outline how resources will be allocated to different project activities and tasks.
Step 3. Define the rates or costs associated with each resource. Outline the cost estimation techniques you are going to use for predicting the cost of the tasks such as analogous or parametric estimating.
Step 4. Create a project budget. Breakdown the project by project phases, deliverables, or cost categories. This serves as the cost baseline for tracking and controlling project expenses.
Step 5. Set the cost control thresholds. It defines the highest or lowest spend allowed for an activity in your project. It can be a percentage of the total budget or cost categories.
Step 6. Define the key performance indicators to track project progress and how project performance related to costs will be measured. It includes techniques such as earned value management (EVM).
Step 7. Define the project management tools you are going to use to track and manage project costs.
Step 8. Determine how you will and how often you report your project progress on project status, costs, and any deviations from the plan to the stakeholders.
Step 9. Predict the risks and define the mitigation strategies or cost control activities you are going to adopt to bring the project in as budgeted or request for budget expansion.
Best practices for project cost management
Managing the project cost can be challenging. Here are some of the key best practices to keep your project costs under control:
1. Manage project costs throughout
Most beginners make the mistake of considering cost management as a one-time event that needs maximum attention at the beginning of the project. But, it is a continuous process of planning, evaluating, tracking, controlling, and managing the costs of a project.
2. Keep in mind project budget is still an estimate
A perfect project plan does not exist. Keep in mind that the project cost you are predicting after using all the cost estimation techniques is still an estimate. With alterations in project factors, project cost needs to be re-estimated.
3. Manage scope and schedule with cost
Cost is not an independent project factor. It directly depends on the scope, schedule, and quality of the project. You need to integrate cost management with other project management processes for effective project management.
4. Keep stakeholders engaged with clear communication
Key stakeholders are the ones who are most concerned about the project’s bottom line. Involve stakeholders in planning the budget, mapping out the resource requirements, and re-estimation of the project costs if required.
Ensure clear communication with stakeholders about the budget and cost expectations throughout the project.
5. Use project management software
Project cost management for complex projects on spreadsheets is not easy. It will take time, and manual effort, and be prone to errors. Use a dedicated project management software that helps you document, implement, and track project cost management activities with ease and efficiently
ProofHub is an amazing all-in-one project management and team collaboration software that can help you with project cost management.
Here is how ProofHub can help you:
- You can break a project into tasks and subtasks with centralized task management and assign the resources to each task.
- You can create a workflow to define the series of tasks and visualize the project roadmap on the Gantt chart
- You can manually add the budget of each task and estimated time to create an overall project budget
- Project status reports help you to see the project progress by Project status, Task completion, Resource utilization, Time utilization, and Time logged for tracking
- You can brainstorm with stakeholders on project cost estimates using project discussions
- You can share all the project files under one place to document the project cost management plan
- You can accept requests from clients for change in scope with forms
Conclusion
Cost is the most important factor in a project. It is because the end goal of any project is to make profits. You complete a project on time, keep a project’s scope in check, and build a quality project to ensure that you make a profit from the work you are doing.
Project cost management focuses on the processes to complete a project within budget. With the help of the right project cost management techniques, tools, and software, you can create a project cost management plan to ensure project success.
Related articles
- What is project management – Definition, best practices, benefits, and features
- Reasons for cost estimation inaccuracies in project management and how to avoid them
- Project management plan – Everything you need to know about
- 11 Most used project management charts by managers
- 7 Big project management conflicts & ways to solve them
- 15 best project management apps for 2026
FAQs
Who is responsible for cost management in a project?
A project manager is responsible for cost management in a project. Project managers use knowledge of project management, experience in planning projects, and cost estimation techniques to accurately predict, track, and manage project costs.
Which project tools help with cost management in project management?
A project manager can use a variety of project tools and techniques to effectively manage the cost of a project. The most common project cost management tools include Three-point estimating, Reserve analysis, and Earned value management.
What is the first step in project cost management?
The first step in project cost management is to plan the resources. It is because without knowing the resource requirements it is hard to estimate the project costs. Project resources include material, equipment, human resources, technology, and infrastructure.
How to project costs accurately?
The best way to estimate a project’s costs accurately is to use cost estimation techniques after determining the scope of the project using a work breakdown structure. The most commonly used cost-estimation techniques are Analogous estimating, Bottom-up estimating, Parametric estimating, and Three-point estimating.
How to communicate project cost objectives to stakeholders?
The best way to communicate project cost objectives to stakeholders is to involve stakeholders in the project cost planning. Once they have a clear understanding of the project scope and resource requirements, they will be able to understand the project cost objectives.
What are the three pillars of costing?
Based on the types of project costs, the three pillars of costing are direct costs, indirect costs, and overhead costs. Direct costs are directly attributed to the project, indirect costs are not directly attributed to the project but are required for project operations, and overhead costs are also not directly related to a specific project but support the overall operations of an organization.
What are the basic principles of cost management?
Cost estimation, cost budgeting, and cost control form the basic principles of project cost management. You need to create a project budget that adequately supports project activities and ensures project completion.

