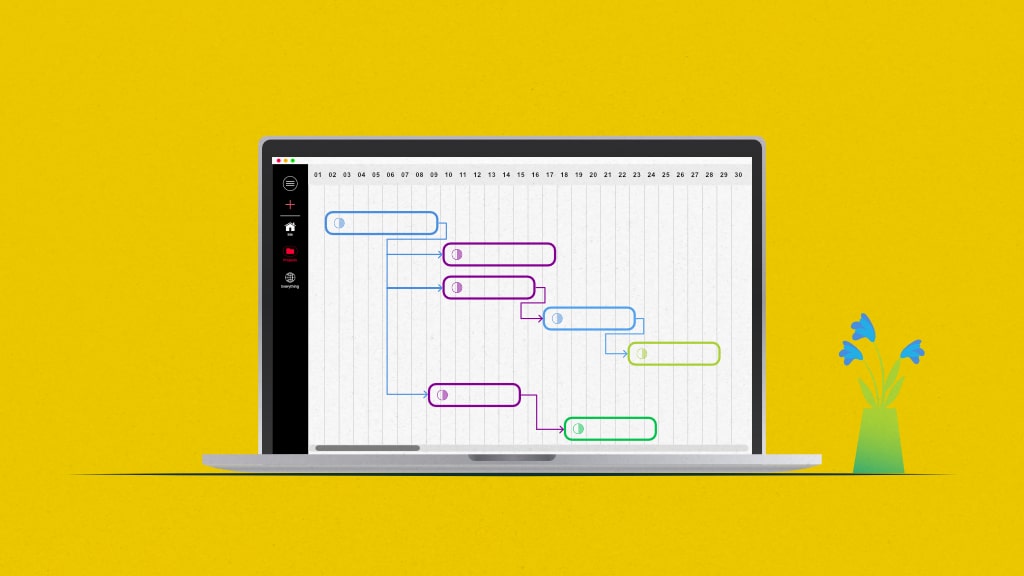
Every project comes with a baggage of project dependencies, but don’t worry, there’s a method to this madness. Let’s uncover how project or task dependencies are an indispensable part of project management and how these can affect the functioning of your team as a whole.
What are project dependencies?
Project dependencies refer to the relationships between tasks or activities within a project, where the completion or timing of one task depends on the completion of another.
Max Wideman’s Glossary describes project dependencies as the “relationships between products or tasks”.
Dependencies in a project occur when a certain task requires the completion of some other task/set of tasks for their commencement.
For example,
The cake can be baked and the icing can be prepared by a team simultaneously, thus, being independent tasks. However, you cannot bake your cake unless you have preheated the oven at an earlier time, thus making one task dependent on the other.
Or, for instance, speaking in content marketing terms, a piece of content cannot be published until the writers’ team can provide appropriate content.
From the above-mentioned examples, it is clear why dependencies exist.
In complicated projects or in projects that are planned on an enterprise level, we tend to pick a direction, map out a definitive number of tasks, define assignees, and set deadlines and that’s it—we’re good to go.
But, are we?
What if 2 out of 10 people from the writing team are on leave?
How will the tasks that are next in line be delivered on their deadlines?
Seems like the whole project’s timeline is going to be sabotaged. Does that alarm you? It should. This could happen to any team within any project.
Dependencies are easy to overlook since plans are mostly made keeping the best-case scenarios in mind.
What if your people were to fall sick?
What if your office needed a sudden renovation?
What if you run short on resources?
What if the client suddenly changed the whole scope of the project?
These are the kinds of questions we forget to consider while building up the plans for a project. And, it is also why project dependencies need your undivided attention.
Tune out the distractions and visualize your tasks through colorful Kanban boards with ProofHub. Sign up today!
Types of project dependencies with examples
You now know what project dependencies are and some important terms related to them, but do you know about different types of dependencies in project management are there? Dependencies vary as several internal or external factors affect them.
Let us take a look at some major types of project dependencies that are commonly witnessed in project management.
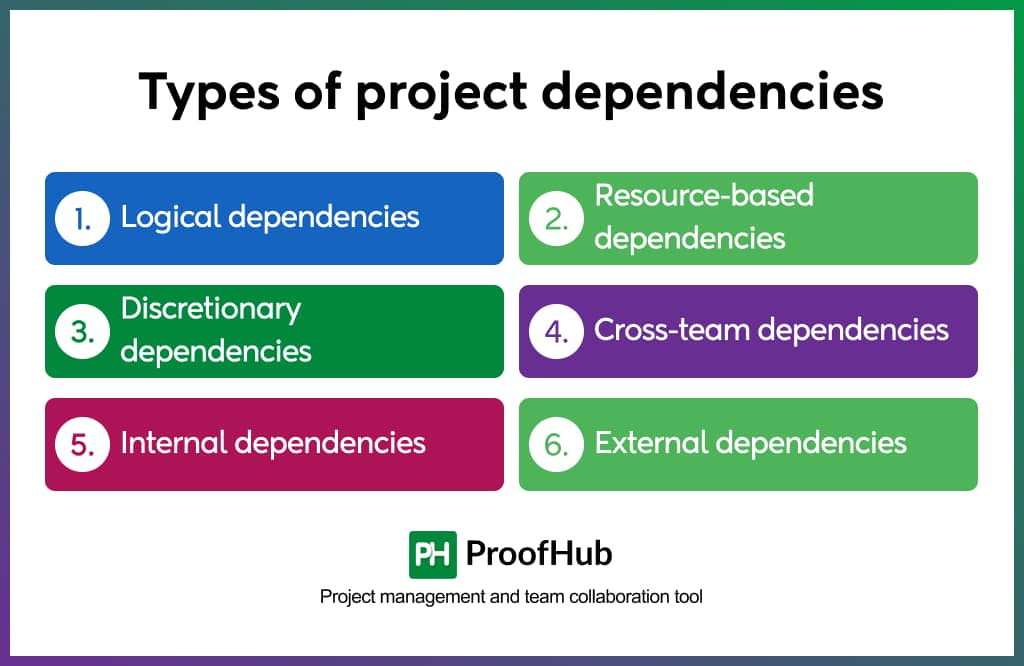
Logical dependencies
Logical or Causal dependencies are quintessential to project management and cannot be avoided as these are necessary for project completion.
Tasks with logical dependencies cannot be performed simultaneously. Without the completion of a preceding task, the succeeding task cannot be started.
Example – You cannot publish a blog on your website straight away. It has to be written, reviewed, and edited before it is ready to be published.
Resource-based dependencies
Project constraints influence resource-based dependencies. This type of project dependency is witnessed when two or more tasks require the same resources for completion. Since there are limited resources, two tasks will be dependent on the completion of the other.
Example – There’s only one meeting room and two teams need to conduct a team meeting. So, Team B will have to wait for the meeting of Team A to be completed, so they can use the meeting room.
Discretionary dependencies
Discretionary dependencies, also known as preferred or soft logic dependencies, are those that are at the discretion of project teams, other stakeholders, and best industrial practices. These are not necessary for project completion but can help improve the quality of project deliverables.
Example – A content manager may review and edit a blog before forwarding it to the marketing team for publishing. This workflow step ensures error-free content is published, but the blog can still be published without the review process. However, the quality of published content may not be up to mark.
Cross-team dependencies
Cross-team dependencies are commonly witnessed in large-scale organizations where teams from different departments work together to complete a single complex project. In this case, teams depend on each other to achieve a common goal i.e. timely project completion and delivery.
Example – Vartika Kashyap, Chief Marketing Officer at ProofHub, often tackles this type of dependency when working with the digital marketing and content team. To create factual, well-researched content for the target audience, digital marketers need to check the content for structure and SEO friendliness.
In ProofHub’s Board view, tasks are divided into stages and selected people are assigned to tasks for creation and review. It is easy to drag and drop tasks to the next stage so everyone can have a clear view of the task’s progress.
Internal dependencies
Internal project dependencies are those that project teams have complete control over and there’s no dependence on outside parties. Internal dependencies are when two tasks or activities within the same project are dependent on each other and there’s no reference to external projects and activities.
Example – The Quality Analyst team is not in a position to test software until the development process is finished.
External dependencies
Opposite to internal dependencies, external dependencies are those when project teams have no control over external factors and are not in a position to do anything to escalate the project’s progress.
Although most project activities are controlled by internal teams. Many external factors can affect the progress of the projects such as client approval, vendors, tools, and others.
Example – A project team cannot start working on a project until the client (external party) gives the go-ahead to the team. In this case, a project team is dependent on external parties i.e. client to start working on a project.
Understanding task dependencies is just as important as understanding project dependencies. Let’s take a closer look at what these are below.
Task dependencies in project management
Some dependencies only apply to the two tasks at hand. The most common forms of task dependencies are listed below:
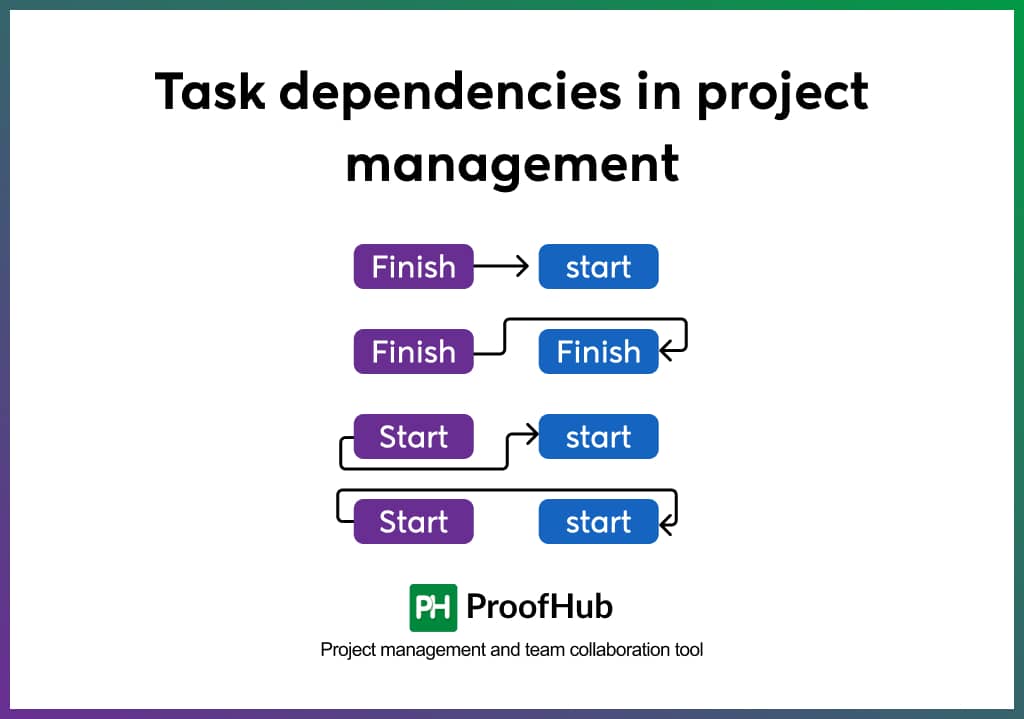
Finish to Start (FtS)
This task dependency is the most prevalent. Task A must be finished before Task B can begin.
Finish to Finish (FtF)
Before Task A is finished, Task B cannot be finished. This frequently occurs with tasks that have subtasks.
Start to Start (StS)
Task B cannot begin until Task A begins under this model. These are for tasks that need to be completed concurrently.
Start to Finish (StF)
For Task A to be finished, Task B must begin. This is crucial in circumstances where there must be overlap.
Ways to manage project dependencies
“Give me six hours to chop down a tree and I will spend the first four sharpening the axe.” – Abraham Lincoln
Instead of jumping to the execution stage, one needs to be prepared for everything, take time to build a foolproof plan, and sharpen one’s proverbial axe more comprehensively.
Therefore, project dependencies or not, one needs to make sure that the whole process goes smoothly, and that everything comes together in the end, no matter how many adversities strike you on the way.
Here are some examples of what you can do:
Active risk management
Discrepancies are bound to come your way as a project takes shape, however, we must always have a fallback plan for these with some risk management strategies.
Risk management is a longtime investment and a real asset to your planning process. It can help you assess, identify, control, and manage threats to your project before they even happen.
For risk management analysis and execution, we need to have certain parameters in place that can help us foresee damage and thus, keep a store of extra resources. Here’s what you can do to keep that in check:
- Use Gantt charts to map out your projects and keep tabs on project dependencies.
- Use tracking software to track progress and time activity to ensure everything is working as it is supposed to.
- Assign risk probability to tasks using a scale of 1-10 or whatever else feels appropriate.
- Assign risk impact on a similar scale to all particular tasks, especially ones that carry dependencies.
- Estimate and map out the timing of the risks that could cause a significant impact on the project timeline.
While you define tasks, and their deadlines, and manage project dependencies, you will also run into situations that can muck up your project, therefore, it is wise to invest your time and resources into doable risk management measures.
Also read – 11 Best software for risk management
Using gantt charts
To manage a particular aspect of a project, you need to be able to see what you are going to manage. For example, project dependencies can be managed in a better way when you can visualize them. That is where Gantt chart tools come in handy.
Gantt charts, as we talked about before, can help teams track and manage project dependencies with ease. Here’s why Gantt charts work:
- These help you visualize tasks.
- These help you set deadlines and get a bird’s eye view of the whole project.
- These help you manage time and overlook the project timeline.
- These help you maneuver through all the tasks and modify task durations and project dependencies.
- These help you assign tasks to your teammates and get quick access to important files as well as feedback.
Making use of timesheets
Time tracking is another measure one must take seriously while managing discrepancies and project dependencies. Time tracking tools or elaborate timesheets can help you with time and other resources are being used.
Timesheets help keep a record of how much time is going into the progress of your project. Apart from that, it will also help you judge employee performance and track billable hours.
Additionally, timesheets help map out how much progress has been made and how much work is yet to be completed as you compare real-time progress with the initial plans.
This will help you set more accurate time estimates for future projects and help you foresee where improper usage of time could be a major occurrence.
Apart from that, it will also help you overview how much time is being given to specific tasks and thus help you map out how those particular tasks should be approached and hence, completed ASAP.
Timesheets offered by the top time tracking tools out there will, in essence, help you manage time and other resources more efficiently. Which, in turn, will help you make sure that everything is going according to plan.
Transparency within teams
Another practice that will help you ensure the smooth management of tasks and dependencies is enforcing transparency in the workplace.
Did you know?
> 50% of full-time employees feel that their performances are being held back due to the lack of transparency at the workplace.
> Over 46% of employees out there say that the lack of transparency at their former workplace is what drove them to find new jobs.
> And, 70% of workers state that they feel more connected to their jobs and engaged in their work when the senior management communicates openly with them.
Transparency is important because:
- It keeps everyone on the same page.
- Lowers the chances of miscommunication and confusion.
- Keeps everyone informed.
- Hence, helps you save time and be more efficient.
Here are some steps you can take to ensure transparency in your workplace.
Use a communication/collaboration tool to be in constant contact with your team: These will help you out no matter if you are working remotely or from your shared office space. You can trust these tools to actively help you exchange ideas, updates, important reference links, and more on the go.
For this, you could use software platforms such as Chanty and Troop Messenger.
Have a daily 15-minute stand-up meeting: Stand-up meetings are the kind that are more popular within Agile teams that follow the Scrum framework. These are important 15-minute meetings that help bring the whole team up to speed about what has been achieved, what has been happening, and what is yet to be done.
These two points will help you make significant changes in the team culture of your team. Additionally, this improving transparency will help you foresee trouble and deal with inconsistencies and other issues with much more ease.
Setting weekly goals
This might come as a surprise to you, but setting weekly goals removes all reasons for keeping track of project dependencies.
Here’s how:
1. Weekly goals will help you focus on little portions of the projects, minuscule tasks that can be mapped out beforehand according to their urgency and priority.
2. These goals will help the team focus more on the task at hand. Therefore, there is no chance that they would get overwhelmed by the pressure of the upcoming tasks.
3. Also, weekly assigned tasks will make it easier for the reviewing party to provide feedback in a more timely manner.
But setting weekly goals isn’t as easy as it sounds. Anyone can set goals, but the thing is, that these should be doable. Here are two things you need to keep in mind while setting weekly goals:
- Make sure that the tasks to be performed in the coming week are in order of priority.
- You must provide a realistic deadline for these tasks to ensure that these, indeed, should be completed within the week.
- Document everything and constantly record progress.
Useful tips for project dependency management
Dependency management in projects is not straightforward and there’s no one-size-fits-all solution for dealing with them effectively. Every project manager deals with dependencies differently, depending on the project requirements and conditions.
That said, no matter what the situation is, certain strategies can help you navigate smoothly through this complex path and set your project up for success.
Let’s have a look at them.
Manage tasks smartly with project management software
Project dependencies are about tasks and their inter-dependencies. It’s not easy for project managers to keep track of all tasks while managing multiple projects simultaneously.
This is where using an easy-to-use project management and team collaboration software like ProofHub can help you with dividing tasks into subtasks, allocating them, setting deadlines, and tracking their progress at every stage.
It ensures a clear division of job responsibilities and keeps things transparent within the team.
Switch from Waterfall to Agile methodology
Traditional waterfall methodology might create more bottlenecks and dependencies as you don’t get client feedback at every stage. It can result in making last-minute changes to the project as it nears completion.
Transitioning to Agile methodology can help your organization a lot of valuable time and money as your team receives feedback from clients and other stakeholders at every stage, which ensures that the project is executed as planned right till the completion and delivery.
Maintain a smooth flow of communication
Consistent communication is the key to effective project dependency management.
Team members, clients, and other stakeholders should be on the same page and stay in the loop at every stage of the project for timely exchange of information, review, feedback, and approval.
Depending on the type of information, project managers should use different communication tools such as Instant chat, Discussions, Real-time updates, Video conferencing, etc.
Brainstorm potential risks and challenges in a project plan
When setting up a project plan, you should have a meeting with your team members, clients, and stakeholders to brainstorm all potential risks and challenges in a project plan.
The point of this meeting should be to get multiple perspectives onboard on possible disruptive circumstances and find solutions to manage the effect of blockers on project constraints and dependencies.
Time tracked is time saved; Sign up for ProofHub and make sure every second is productive! Try ProofHub for free
Key project dependencies terminologies
Let us break down a few “key terms” related to project dependencies. It’s important to understand these terms before we dig deeper into the subject.
Constraints
In project management, dependencies and constraints go hand in hand. In simple words, ‘constraints’ are defined as restrictions within which tasks and projects are to be completed.
A manager must adhere to these restrictions, which usually are in the form of – cost, project scope, and time. In some cases, project dependencies occur due to certain constraints.
Also read: Decoding the project management triangle
Lead and Lag
‘Lead’ and ‘Lag’ are two common terms in project dependencies. Lead is the time by which a succeeding task gets advanced concerning the preceding task. This concept applies only to tasks connected with ‘finish to start’ relationships.
For example – Task B is scheduled to start when Task A is completed, which is within 6 days. However, Task A completes within 3 days and the succeeding Task B starts, which means that Task B has a lead time of 3 whole days.
‘Lag’ is exactly the opposite. In this concept, the succeeding task is delayed due to a delay in the completion of the preceding task. Lag is not desirable as it can lead to project delays.
Critical path
A ‘critical path’ can be defined as the sequential chain of activities that lead to project completion. In case any task in the chain gets delayed, it affects the entire chain of events and the project deadline.
Also read: Critical Path Method – A Comprehensive Guide for Managers
Blockers
As the term suggests, ‘Blockers’ is anything that prevents the timely completion of tasks and projects. Blockers can be internal (within the organization) or external (outside the organization).
How to manage project dependencies in ProofHub?
A project consists of various tasks that are to be completed on time to ensure timely project completion. While some tasks are independent, others are interdependent i.e. tasks are dependent on each other to be completed successfully.
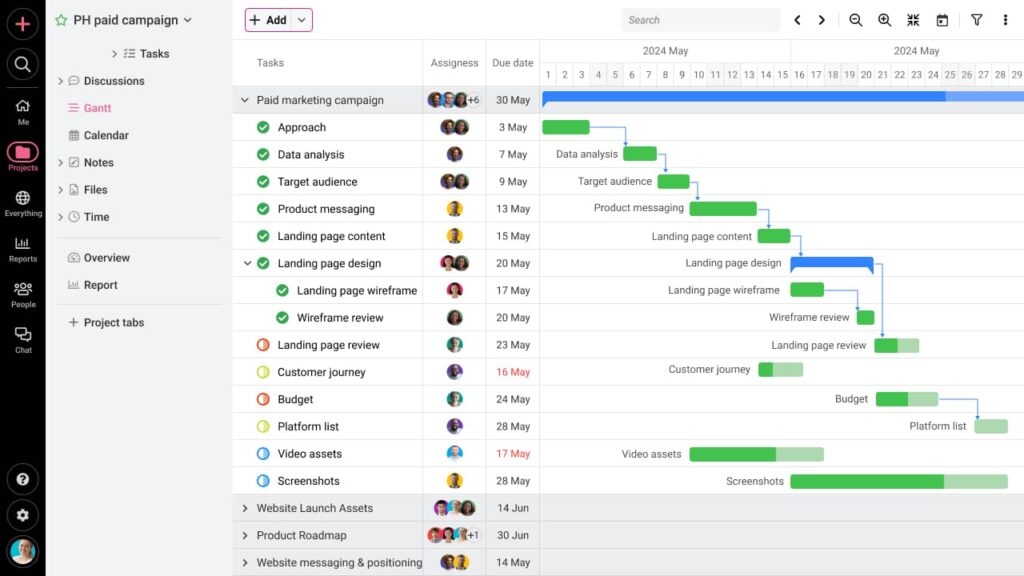
Using ProofHub’s Gantt charts, you can set task dependencies in a project. Once dependencies are set, you don’t need to change every task date in case the starting task is delayed. All dependent tasks will get dragged along the project timeline along with the first task.
Project dependencies on Gantt charts offer you a clear view of how the project is progressing ahead.
Steps to set project dependencies on a Gantt chart in ProofHub
Step 1. Add tasks and task lists to Gantt charts, and plan and schedule the order in which you want tasks to be completed.
Step 2. Assign tasks or subscribe the entire task list to an individual or multiple people. Every team member knows what tasks to work on, and when to start and complete them.
Step 3. Choose the task for which the dependency needs to be set by “clicking on the small circle” next to the task. Drag it to another task to set dependencies between tasks (See the figure below for reference).
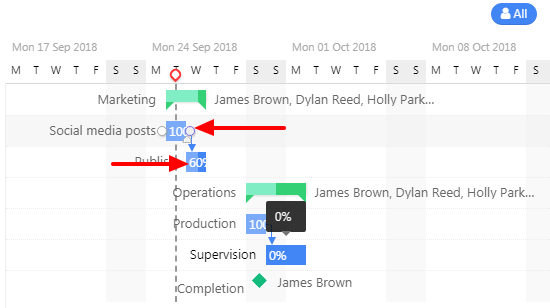
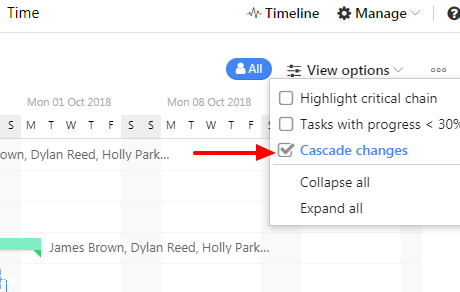
Step 4. In this case, the second task you dragged will be dependent on the first task. However, you would need to enable “cascade changes” to enable dependencies. To do this, you need to select “View options” at the top-right of the page and check off the Cascade changes option from the list. See the figure below for reference.
Want to experience yourself – Try ProofHub for free
Conclusion
Understanding and managing project dependencies is crucial for ensuring the project’s success. By identifying and tracking dependencies early on, you can minimize risks, optimize resource allocation, and maintain project timelines. With careful planning and proactive management, project dependencies can be navigated successfully, leading to smoother project delivery and ultimately, achieving project objectives. We hope this article has improved your understanding of project dependencies.
FAQs
What are common project dependencies?
The most common project dependencies are – Finish to Start, Finish to Finish, Start to Start, and Start to Finish.
How do you identify external dependencies in a project?
To identify external project dependencies, you should:
1. Create a map of project tasks
2. Mark tasks that the team cannot perform
3. Map out major steps needed to complete the project
Are constraints and dependencies the same?
No. Dependencies are the order of tasks whereas constraints are project limitations such as limited time and funds.
How do you manage dependencies?
1. Identify dependencies and constraints.
2. Add dependencies.
3. Calculate the critical path.
4. Share with stakeholders.
5. Track dependencies.
What are Gantt chart dependencies?
A Gantt chart dependency refers to how project tasks are related to each other and each task is represented as horizontal bars that show task duration.