Project management is the process of managing project activities to complete a project on time and within budget to achieve defined goals. This is the simplest and easy-to-understand definition, but it does not teach you project management. To apply project management to real projects, you need to learn various skills, tools, and techniques.
Being the CEO of a project management software company, ProofHub, for over 15 years, I have gained some unique insights into project management that can help you in managing projects in the real world.
In this post, I have shared those insights and explained project management in a way that adds value to you. You will get to learn about the basics of project management— definition, purpose, phases, benefits, and methodologies, how to become a project manager, and the role of project management software.
Let’s start with the definition of the project first!
A Free guide to help you with proven ways to lead a project from start to finish, without confusion or jargon.

What is a project?
A project is a set of tasks that needs to be completed to achieve a certain outcome. However, not all sets of tasks are projects. For a set of tasks to be qualified as a project, it should have a unique outcome and have a start and end date.
People usually confuse a project with a process. Both have a series of tasks and a timeline, but the process is repetitive and produces the same result. In contrast, a project is a temporary endeavor with unique outcomes that have not been created.
Let’s understand it by an example:
Project: Create a software
Creating software is a project because it has unique outcomes and a defined start and end date.
Process: Customer support operations
Customer support operations are a process because they always result in the same outcome, which is customer support, and they repeat and continue.
Despite having a series of tasks, both are not the same.
What is a task?
A task is an individual and independent unit of work in a project that has a defined start and due date. It may or may not produce the same outcomes. Thus, it is different from a project in magnitude, dependencies, and outcomes.
What is project management?
Project management is the process of planning, organizing, and managing project activities in order to achieve intended outcomes.
Quote: The purpose of project management is to complete a project within budget and time of defined quality on the agreed scope.
The standard definition of project management by the Project Management Institute (PMI) says, “Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to achieve the project objectives. It guides the project work to deliver the intended outcomes and meet or exceed stakeholder needs and expectations from a project.”
The PMI or the Project Management Institute is a not-for-profit organization that provides knowledge resources, community, and certifications to train and educate project managers.
It is the highest authority in the field of project management which has created A Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK®) to provide project managers with the fundamental practices needed to manage projects and achieve results.
Read more: Project management tools and techniques to use in 2025
What is the importance of project management?
Project management plays a key role in making projects successful. Have a look at the five key points reflecting the importance of project management.
1. Provides a clear roadmap
Project management involves defining the requirements of the project and creating a plan to convert those requirements into measurable tasks before execution. This creates a clear roadmap for the project team to follow. It results in less confusion about how the project will progress and the project team can approach a project more confidently and manage time effectively.
2. Define key roles and responsibilities
Project management includes clearly defining the roles and responsibilities of each individual in the project and assigning the owner of tasks. This provides clarity to the team members on their roles and what is expected of them. Thus, they can be more accountable and better contribute to the project’s success.
3. Facilitates teamwork
Project management brings all the project work to a centralized and transparent place. This enhanced visibility and free flow of information brings everyone on the same page, improves team communication, and encourages better collaboration among team members and stakeholders. This results in better teamwork, increased accountability, enhanced trust, and improved productivity.
4. Manage project risks better
Project management involves planning for the project risks before execution and continuous tracking of the project progress for improved visibility. This helps you identify the deviations early on and predict the bottlenecks. Thus, you can take prompt action to resolve issues before they become bigger project risks.
5. Resource optimization and better predictability
Project management involves breaking a project into small tasks and defining the dependencies between tasks. Thus, you can easily calculate the resources required for a project and predict when tasks will be completed. This leads to better resource allocation and accurate estimates.
6. Ensure quality deliverables
Project management follows the strong process of quality management. It includes clearly defining the acceptance criteria of each task and getting approval from the stakeholders before submission. This helps you ensure the project meets the quality requirements and reduces the risks of project failure because the expectations of clients are fulfilled.
7. Reduce the risk of project failure
Project management can help you reduce project risks by clearly outlining the project requirements before the execution of the project or taking feedback throughout the project. This helps ensure project requirements are fulfilled.
What are the benefits of project management with real-life examples?
Project management offers a range of benefits due to the clarity and the order it provides to projects. Have a look at the key benefits of project management.
1. Brings clarity to complete a project on budget and time
Project management breaks a large project into small parts with clearly defined timelines and task owners. This makes it easy to track the progress, manage tasks, and reallocate resources to complete a project within budget and time.
Example 1:
Say you are developing new software, and the client requires you to get it ready by Q2 next year. To achieve that, breaking the project into phases like design, development, testing, and deployment with each phase having a fixed timeline helps you stay on track.
2. Manage ongoing project risks to prevent failure
Project management involves planning for the project risks before execution and continuous tracking of the project progress to keep project cost, schedule, and progress in check to deal with ongoing risks. This holistic approach helps you manage project risks better and complete projects on time and within budget.
Example 2:
Picture yourself organizing an event with a set budget of $20,000. If the scope expands to include extra catering services, you will need to re-evaluate the cost. In this situation, you either need to find additional funds or adjust other parts of the event to stay within budget. Carefully managing project risks ensures that you don’t run out of resources halfway through the project.
3. Improve operational efficiency and save from unnecessary costs
With a clear roadmap, project team members focus on following the plan and getting work completed. They spend less time figuring out and planning and better manage their time and resources with a clear plan. This helps improve operational efficiency, resulting in savings from unnecessary costs.
4. Brings everyone on the same page
A project plan provides the same information to everyone. This helps bring everyone on the same page. Along with regular meetings, updates, and progress reporting, project team members can easily clear all the confusion and stay informed and involved throughout the project life cycle, leading to improved collaboration.
5. Meets client needs
Project management irrespective of the methodology, Agile or Traditional, follows a structured approach to managing projects. This helps you meet the client’s needs with a better understanding of the needs and continuous involvement of clients for approvals.
Not just that clients, project methodologies like Agile involve end-users too. Thus, you can deliver products or services that satisfy clients’ and end-customers’ needs.
Example 3:
Let’s say a mobile app that your team builds meets every feature listed in the scope. However, some users find the app glitchy or slow. Agile project management prevents project failure with continuous feedback from customers. This makes sure the project meets both functional and performance standards.
Read more: Traditional vs Agile project management method: Which one is right for your project?
What are the key elements of project management?
The key elements on which project management relies are scope, budget, time, and quality. Throughout the project, a project manager seeks to manage these aspects of the project to ensure a project meets its intended objectives.
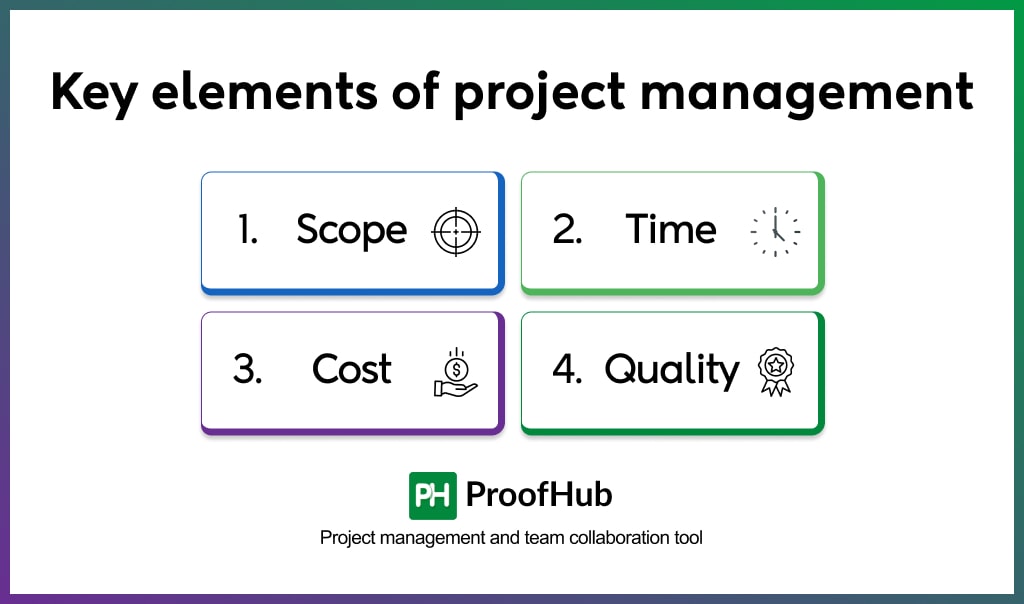
These elements, excluding quality, are popularly referred to as the triple constraints of the project which are represented and managed using a project management triangle or iron triangle, with quality at the center of the triangle. Let’s understand what each element refers to in project management.
Scope
Scope defines ‘what needs to be done’. It includes clearly defining the project’s deliverables, features, functionalities, and limitations. Effective scope management is necessary to make sure all stakeholders are aligned on what will be delivered.
Time
Time represents the duration within which the project must be completed. Through project scheduling, managers create a time-bound roadmap for the whole project.
Cost
Cost defines all types of project costs such as personnel, materials, and equipment. Changes in scope or schedule can impact the overall cost of the project. Through project cost management, a manager tries to keep the project costs in check.
Quality
Quality defines the standards the project must meet to satisfy stakeholders. It is the fourth element of the project that directly defines the success of the project. Because if stakeholders are not happy with the final output of the project, there is no point in balancing the scope, cost, and time. Thus, effective project quality management is necessary to ensure project success.
Every project is bound by these four core elements. Modifying one automatically changes the others. That’s why project managers throughout the project manage these elements to mitigate risks and achieve project goals.
10 knowledge areas of project management
The way to manage key elements of project management is defined in the 10 knowledge areas of project management.
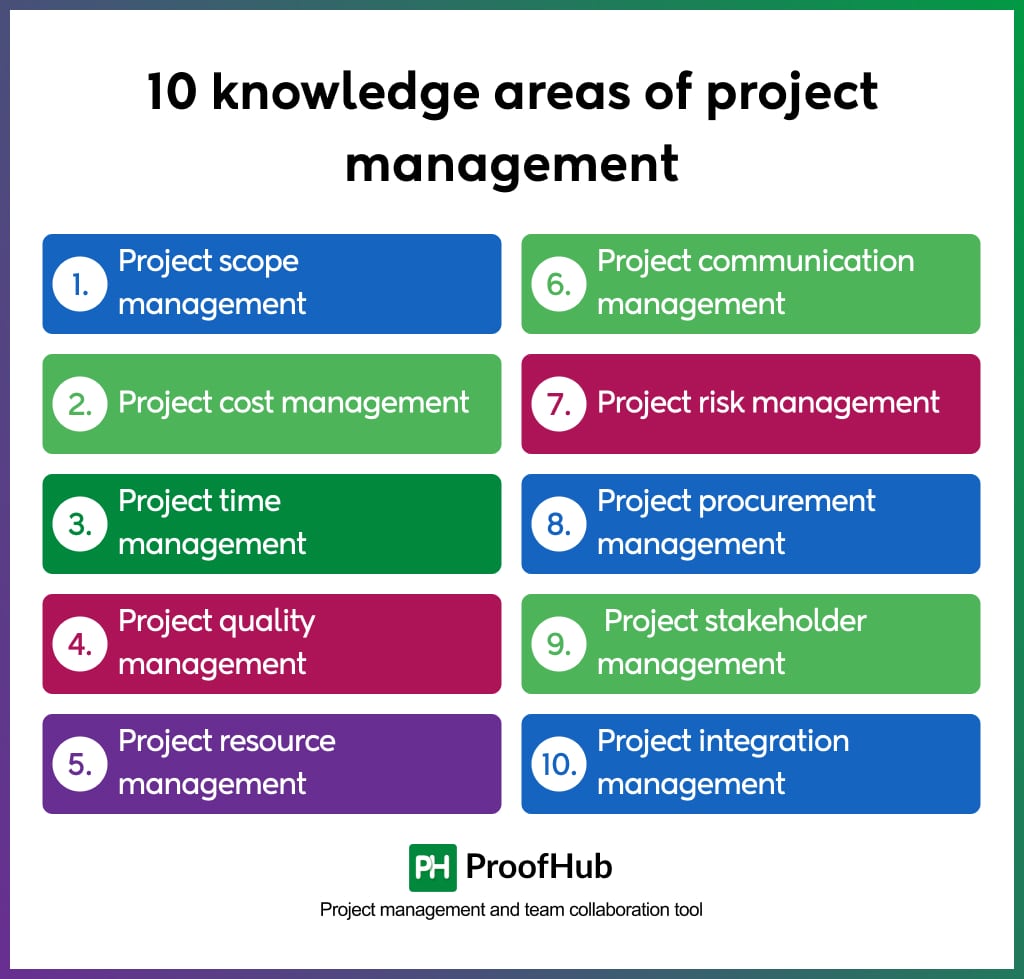
These knowledge areas define the methods, tools, and techniques. Let’s learn about them briefly.
1. Project scope management
Project scope management involves defining and managing what is included and excluded from the project’s boundaries. It starts with clearly outlining the project’s objectives, deliverables, and boundaries to ensure a shared understanding among stakeholders.
2. Project cost management
Project cost management covers the financial aspect of a project. It includes defining all the costs related to the project including human, equipment, technology, and infrastructure.
3. Project time management
Meeting deadlines is crucial for project success. Project time management involves planning, scheduling, monitoring, and controlling all the activities that need to happen to complete a project on time.
4. Project quality management
Project quality management is a set of practices that ensures a project consistently meets predefined quality standards throughout its entire lifecycle.
5. Project resource management
Project resource management focuses on making the most efficient use of every resource available in a project. Project resources refer to anything necessary for successful project completion. This includes technical equipment, materials and supplies, human resources, data and information, etc.
6. Project communication management
Breakdowns in the project’s team communication can lead to failure. Project communication management focuses on defining communication guidelines for project teams and stakeholders to streamline project communication.
7. Project risk management
Project risk management is a crucial knowledge area in project management. It focuses on identifying, analyzing, and developing responses to potential events that can impact your project’s objectives.
8. Project procurement management
Project procurement management is the knowledge area that focuses on obtaining all the goods and services that are necessary to your project but are not inherently available within the organization. It involves activities such as sourcing suppliers, negotiating contracts, managing supplier relationships, and processing payments.
9. Project stakeholder management
Project stakeholder management is the area that focuses on identifying and managing the expectations of all those individuals who are impacted by the outcomes of the project.
10. Project integration management
Project integration management focuses on ensuring perfect coordination among other areas for successful project completion. This involves formalizing a project, defining its objectives, and creating a project charter.
What are the five phases of project management?
To manage a project effectively, the PMI has defined a framework of project management process groups, or project management phases. It breaks a project into five phases: initiation, planning, execution, monitoring, and closure.
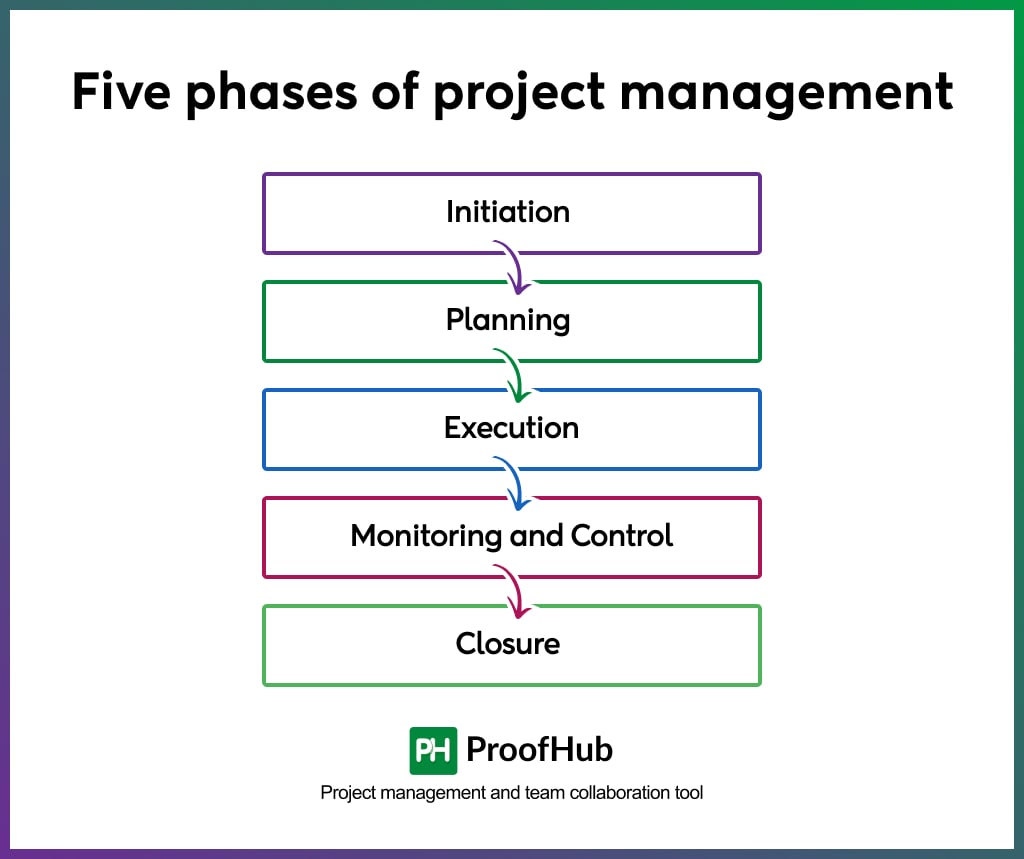
From start to finish, throughout the project lifecycle, these five phases guide a project manager to control the project to complete it within budget and time.
Here are what the five phases of project management entail:
1. Initiation
This phase focuses on defining the project’s requirements, objectives, key stakeholders, feasibility, and initial schedule and budget estimates. It results in the development of a key project document known as a project charter, which outlines the project’s scope, goals, and objectives.
2. Planning
During this phase, a project manager creates a comprehensive project plan. This plan includes the details of the tasks to be completed in a project, project milestones, activities, and timelines, project resource requirements, and risk management strategies.
3. Execution
This is the step where the project team puts the project plan into action. The project manager plays a key role in coordinating resources, including people, tools, and materials, while also ensuring the team is well-informed about their tasks and timelines. This phase involves ongoing monitoring and progress tracking.
4. Monitoring and Control
This critical phase involves actively monitoring project progress against the established plan. Deviations from the plan are identified, and corrective measures are taken to ensure the project remains on track. Moreover, key stakeholders are well-communicated and updated about the changes that happen while executing a project.
5. Closure
The final phase marks the formal end of the project. In this phase, project deliverables are finalized, final approvals and sign-offs are received from the stakeholders, a project is evaluated and lessons learned are documented, and a final review is conducted to evaluate project success.
Read more: 5 phases of project management life-cycle
Most used project management methodologies
The most commonly used project management methodologies are Agile, Waterfall, Lean, PRINCE2, Six Sigma, and Critical Path Method (CPM). But more than project management methodologies, it is important to understand the project management approaches. It is because this will help you make the right decisions on choosing the right project management methodology for your projects.
Here are the three approaches to project management:
1. Predictive project management approach
The predictive project management approach follows well-defined phases, with each phase completed before moving on to the next. It follows a linear and sequential path. This predictable progression makes this approach ideal for projects with clearly defined goals and a stable scope.
Examples of methodologies in this approach:
- Waterfall: Most common in industries where project phases (requirements, design, implementation, testing, deployment) follow a strict order like construction, manufacturing, and IT development.
- Critical path method (CPM): In industries like construction, aerospace, and defense projects to schedule tasks that are critical to project completion, ensuring all timelines are adhered to.
- PRINCE2: In Govt and public sector projects where the focus is on clear roles and responsibilities, making it effective for projects with extensive stakeholder requirements.
2. Adaptive project management approach
Adaptive project management approach takes an iterative and cyclic approach to project management. It includes continuous improvement and adaptation at the end of every cycle.
This type of approach is well-suited for projects that don’t have a clear scope upfront and need to adapt to evolving requirements. It provides the flexibility to accommodate changes on the go and promote customer engagement through continuous feedback.
Examples of methodologies in this approach:
- Agile: Used widely in software development to accommodate rapidly changing requirements.
- Scrum: To tackle tech projects where a lot of cross-functional teams work in sprints.
- Kanban: Common in product development and production industries, Kanban is a visual workflow management tool that allows teams to see work in progress and limit bottlenecks.
3. Hybrid project management approach
As the name suggests, this approach combines the principles from both approaches. It includes blending the structured approach of traditional methodologies with the flexibility and adaptability of iterative approaches.
Hybrid project management falls under this approach and combines elements from different methodologies, either traditional or iterative.
Examples of methodologies in this approach:
- Scrumban: A blend of both Scrum and Kanban, it’s useful in projects that are looking for flexibility in Kanban’s workflow and Scrum’s structure. Most often used in teams transitioning from Agile to Kanban.
- Lean Six Sigma: Popular in healthcare, finance, and manufacturing, It combines Lean’s focus on waste reduction with Six Sigma’s quality improvement techniques.
Biggest challenges a manager faces in project management (+ how to manage)
There are certain challenges a project manager is inevitably going to face while managing projects. Therefore, it is important to understand the biggest challenges in project management so that you are better prepared to deal with them.
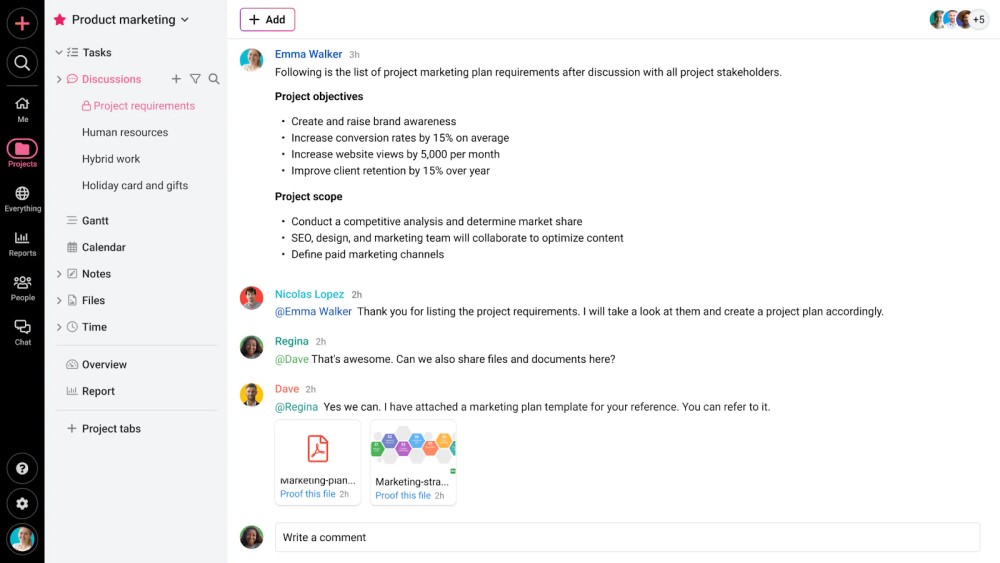
1. Scope creep
The biggest challenge in managing any project is scope creep. It happens most of the time and is almost inevitable. (Scope creep refers to the expansion of the original project requirements.)
Most of the time, it happens because a client does not have an idea of the final outcomes of the project and they keep adding to the project requirements. Sometimes, it happens because of the changing market dynamics such as a change in user behavior and a new launch of a feature from a competitor, leading you to change the scope.
How to manage:
Involve stakeholders during the project initiation and follow Agile project management for execution. At ProofHub, my development team uses Agile project management to ensure key stakeholders’ involvement. The very reason Agile project management methodology came into existence is to provide flexibility to the managing projects in order to accommodate the changing requirements.
2. Setting a realistic deadline for the project
The next biggest challenge even experienced project managers face is setting realistic deadlines and calculating the resource requirements of a project. Most of the time project managers either overestimate or underestimate the resources required for the tasks of the project. These inaccurate estimates lead to delays and project failure.
How to manage:
Use various project management techniques such as work breakdown structure (WBS), three-point estimation, expert judgment, and historical project data.
3. Ensure the team is on the same page
Project management thrives on effective communication, but it is hard to bring everyone on the same page. It is because every individual understands and interprets the roles and responsibilities and project objectives and acceptance criteria of the project deliverables in their way. Thus, this creates conflicts.
How to manage:
Create a shared understanding. Use project management software to bring all the project-related documents in one place and converse with team members to provide clarity on each individual’s role.
4. Lack of clarity on project goals and KPIs in tangible terms
A project manager often finds it difficult to convert the stakeholders’ expectations into the project’s requirements, set measurable objectives, and define KPIs. Thus, this leads to a poor understanding of the project objectives, conflicts, and lack of shared vision.
How to manage:
Use the SMART framework to make the project objectives, goals, and performance KPIs tangible.
5. Keeping the stakeholders engaged with the project
Managing stakeholders is one of the biggest challenges of project management. Here we are referring to end-users also. Lack of engagement of the project stakeholders leads to delays in approvals and unsatisfactory deliverables, leading to project delays and cost overruns.
How to manage:
Create a stakeholder management plan and involve them throughout the project.
All of this requires a deep understanding of the project management and its techniques. Let’s find out how you can become a project manager.
How to become a project manager?
A project manager is responsible for managing the project. They need to understand various project management tools, techniques, and methodologies to manage projects successfully. There are many ways to become a project manager. We have defined the three primary ways.
1. Internal promotion to the role of project management
The most common way to become a project manager is by taking the PM role after gradually taking on more responsibilities in their current roles. I call these professionals accidental managers because they do not come from some kind of business school or certification program in project management. This approach is ideal only for existing professionals.
2. Get certification by Google or PMI
The next most common way to become a project manager is to appear for the certification exam to become a certified project manager. There are two most popular certification programs:
These certifications help you learn skills, gain knowledge, and become a certified project manager.
3. Graduation or diploma course in project management
The least common, but gradually becoming a popular way, to become a project manager is to enroll in a graduation or diploma course in project management from a certified university. It is usually a long program and ideal for the students, while the above-mentioned ways are ideal for the existing working professionals.
After the completion of the degree course, you can get an internship or get a junior-level role in a company to work under an established and experienced project manager.
Read more: How to become a project manager: Top-notch tips and skills
What is the role of project management software in managing projects?
To apply project management to real projects, you need project management software. It provides you with a platform where you get tools to implement project management techniques.
Prior to the project management software, project managers use spreadsheets for recording data, creating project plans, and collaborating with the team. However, learning Microsoft Excel for project management is not easy.
For example, creating a Gantt chart in Excel requires advanced knowledge. I also have to watch multiple video tutorials on how to create a Gantt chart in Excel.
On the other hand, project management software provides you with a centralized platform to create a project plan, facilitate discussions among stakeholders, create and delegate tasks, track project progress, and prepare reports to evaluate project performance. Thus, you can effectively apply each phase of the project management to real projects.
Let’s understand how project management software can help you effectively manage projects.
Manage projects with ProofHub – project management and team collaboration software
ProofHub is an all-in-one project management and team collaboration software that brings projects, team members, and document collaboration to a centralized place.
Here are the key features that can help you with project management to save time and money:
1. Gantt chart
ProofHub helps you create a project plan by breaking a project into phases, tasks, and subtasks. This four-level project hierarchy makes it easy to calculate the time and resource requirements of each task of a project and leads to an accurate estimation of the cost of the project.
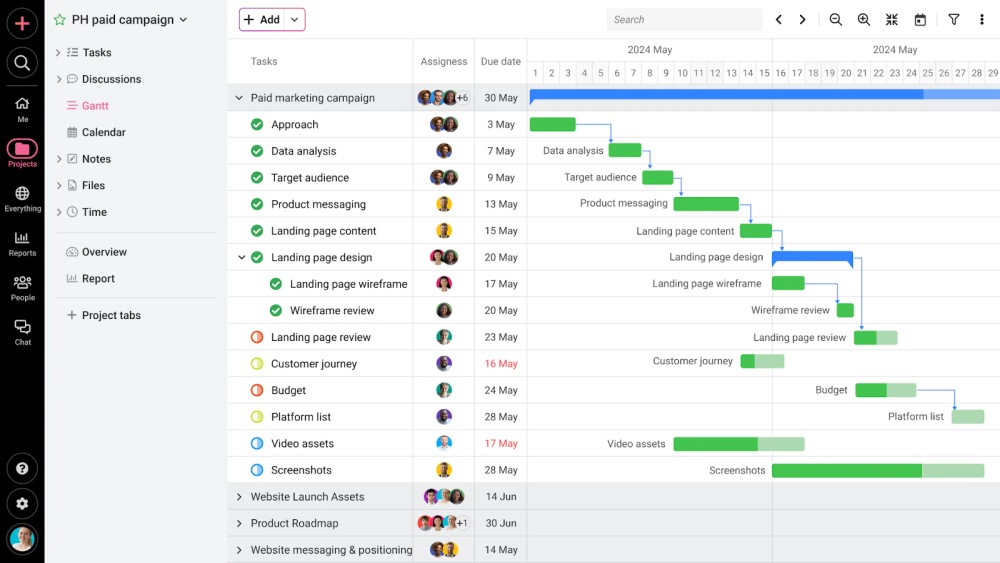
With the ProofHub Gantt chart, you can visualize the project plan on a timeline. Thus, it allows you to identify the overlapping tasks and resources and set dependencies.
You can set milestones, add constraints to the project, and define a baseline to create a standard roadmap for the entire team. Team members can visualize the impact of delay on the project with a critical path.
2. Task management
ProofHub provides you with task management platform features that allow you to set the start and due dates of each task and assign task owners to the tasks. This helps you clarify the responsibilities of each individual in a project.
As you can add all the details of the tasks in project management software, it eliminates the need for emails for task delegation and information sharing.
With ProofHub tasks, you can add task descriptions, attach files, set estimated time and budget, and track the time spent on tasks.
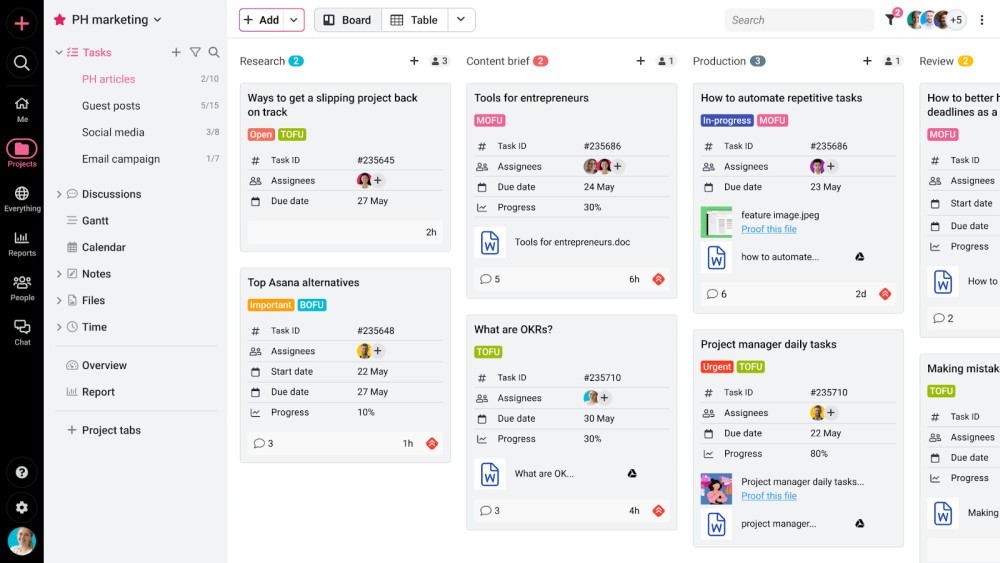
3. Multiple project views
ProofHub provides you with a centralized board where you can see all the projects and tasks of the team. You can see all the projects at a glance from different angles with multiple project views like Kanban and Table and use filters to sort information. This makes it easy to stay on top of task status updates.
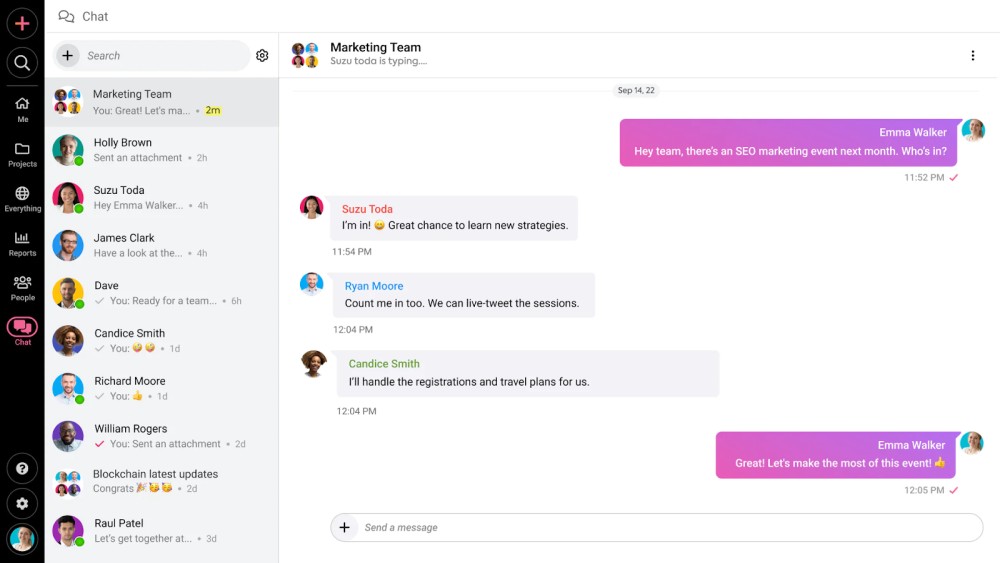
4. Team collaboration
ProofHub provides you with a collaboration platform to communicate and share information with the team. It provides you with tools like real-time chat, project discussion board, task comments, project files, and collaborative notes.

These tools make it easy to work together effectively with a free flow of information and help in improving productivity and quality of teamwork with effective collaboration.
5. Project reports and time tracking
ProofHub helps you monitor and evaluate the project performance with project reports and time tracking. It provides key insights to the project such as budget and resource utilization tracking, number of tasks completed, number of tasks pending, project costs, time spent on the tasks, and resource performance status.
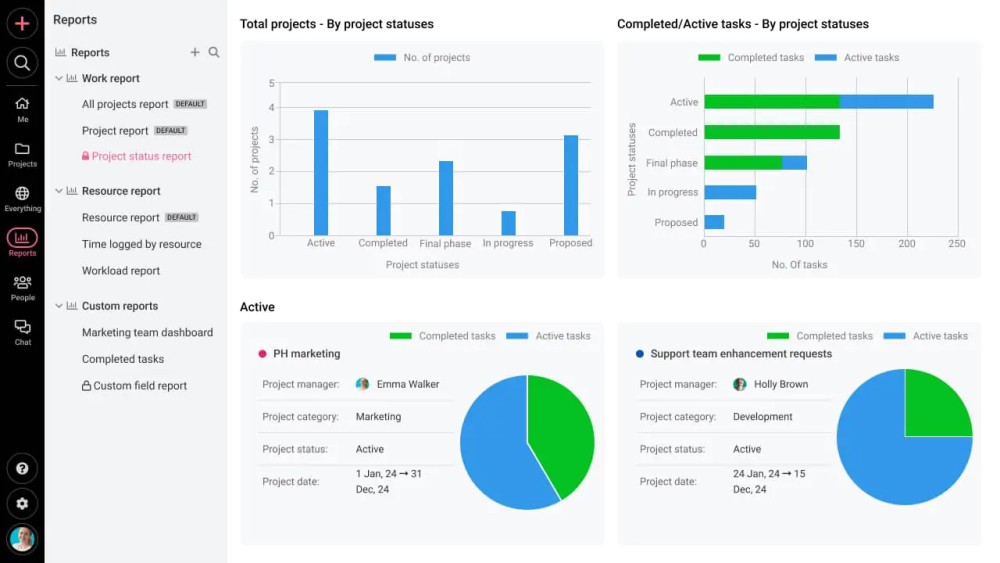
These project reports by various parameters help you take control of the project and make data-driven decisions.
Apply project management to increase chances of project success
Managing a project is a challenging task. There are so many elements to manage that one can easily get overwhelmed. The project management provides knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to manage projects. By building mastery in project management, a project manager can manage projects with standard frameworks and guidelines and use advanced project management software to increase the likelihood of project success.
Frequently asked questions
What are the important roles in project management?
The most important roles in project management include project manager, project sponsor, project stakeholders, project team members, and business analysts.
A project manager is responsible for creating a project plan and executing the project.
Project sponsors have business interests in the project and are responsible for setting high-level objectives.
Project team members are the professionals working on the project.
Project stakeholders are the individuals or groups impacted by the project. It includes end-users, government agencies, vendors, suppliers, etc.
A business analyst deals with clients and collects initial project requirements.
What is the difference between program and project management?
Program management involves overseeing related projects to achieve broader organizational goals. It focuses on the accomplishment of strategic and high-level organizational objectives. Whereas, project management involves the management of individual projects. It focuses on the planning, execution, and completion of project-specific objectives.
How important is certification in project management?
To grow your career in project management, certification in project management is very important. It is because certification proves your skills and knowledge in project management.
What are the tools used in project management?
The most popular tools used in project management are Project Charter, Project Budget, OKRs, RACI, Risk Management Plan, and Statement of Work. If we talk about the software, the most popular tools are ProofHub, Asana, and Wrike.
Who is responsible for managing the project?
A project manager is responsible for managing the project. They oversee everything from creating project plans to assigning tasks, coordinating the team members and stakeholders, monitoring progress, identifying potential bottlenecks, and managing risks to keep the project on track.