The first question that comes to the mind of any beginner is, what exactly is project management? If you look it up, you might find this project management definition: project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet project requirements. That sounds impressive, but this definition leads to many ‘Hows’ for a beginner, such as what skills, which techniques, and what tools.
That’s why in this chapter, we will go beyond the textbook definitions and actually explain project management that a beginner can comprehend and understand.
What is project management?
Project management is the process of managing project activities to achieve the desired outcomes.
To understand this definition better, it is important first to learn why a project is created.
A project is created because you want to achieve certain desired outcomes, a solution to a problem. For example, a mobile app for the company website can be designed to target mobile users.
To achieve those outcomes, you need to work. The activities involved in managing that work are called project activities. For example, arranging resources, coordinating with the project team, and creating a plan.
The management of the complete work of a project including people and resources can be defined as project management.
Thus, project management involves planning, organizing, executing, and monitoring project activities to achieve the desired outcomes of a project. It provides you with tools, techniques, frameworks, and knowledge to manage a project.
To get a better idea of what knowledge of project management focuses on, let’s understand what happens when you want to work on a project.
When you decide to work on something, it results in some natural queries:
- What we need to work on (Scope)
- How much time it will take (Time)
- What will be the cost (Cost)
- What does the end result look like (Quality)
These four questions form the basics of project management, which are also known as the key elements of project management: Scope, Time, Cost, and Quality.
The entire knowledge of project management primarily revolves around the management of these four foundational elements of the project with the purpose of achieving project objectives.
Objectives of any project can be roughly classified as:
- A project should meet its intended goals or defined outcomes
- A project should operate within the boundaries of scope, time, cost, and quality
- Interests and expectations of all stakeholders are served
The role of a project manager is to make sure a project meets its objectives. A project manager uses the knowledge of project management to manage the work, people, and resources involved in a project.
Key elements of project management
Every project has four key elements: scope, time, cost, and quality. These are the foundations of project management. From time to time, you will use these terms in conversations with stakeholders.
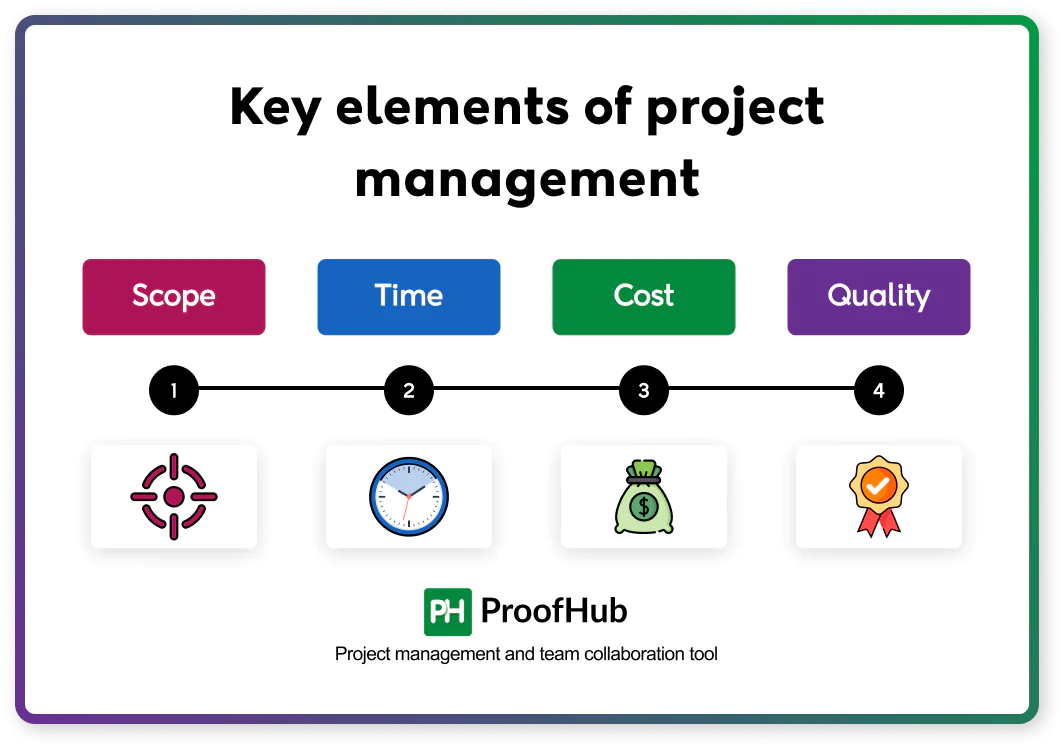
Let’s understand what each element of a project refers to.
1. Scope
The scope of a project defines what needs to be done. It includes defining the project’s objectives, goals, deliverables, and limits. It restricts your project to certain boundaries: what is included and not included.
For example, you are tasked to work on a website redesign project. The scope might include updating the homepage, creating a responsive design, and integrating a blog. Developing a mobile application, however, would fall outside the scope.
A clear project scope provides direction to the team, helps a project manager create a realistic project plan, and ensures all stakeholders agree and align on the project goals.
2. Time
Time of a project defines the timeline you have to complete the project. It includes determining the time required to complete various tasks, phases, and stages of a project. It restricts your project to a specific deadline.
For example, you want to develop a mobile application for the company. Based on the scope, you have broken the project into four phases and estimated the time required to complete each phase based on the tasks. This created a deadline for each phase, which in turn collectively created a deadline for the project.
A well-defined timeline helps you track the project’s progress, identify potential delays early on, and make adjustments to complete the project on time.
3. Cost
Cost of a project defines the budget you have for a project. It includes all types of costs of a project such as labor, materials, and equipment. It restricts your project to a certain budget.
For example, building an e-commerce site might require $10,000 for development, $5,000 for marketing, and $2,000 for testing. A 10% buffer might also be added for unexpected expenses.
Effectively determining the costs of the project helps you ensure a project has sufficient budget to provide the resources required for a project. Having a defined budget makes it easy to track the expenses and guide decision-making to keep the project within an agreed budget.
4. Quality
Quality of a project defines how the outcomes of a project should look like. It includes determining the requirements for the successful acceptance of project deliverables. It creates acceptance criteria for the project outcomes.
Clearly defining the quality requirements helps you create a shared vision for the project team and make sure stakeholders’ expectations are fulfilled.
For example, a client requests a brochure with premium design and precise brand colors. Delivering a design with mismatched colors leads to rework and client dissatisfaction.
What more to learn?
If you clearly observe the above four project management components, you will find these are putting restrictions or creating boundaries for the project. That’s why they are also called project constraints.
Every project is bound by these four key elements and all of these are interconnected. Change in one leads to change in others.
For example, if you add to the requirements of the project, it means more time and resources to complete the increased work. A change in the scope leads to a change in the cost and time. Thus, it can decide the success or failure of the project.
This relation between the scope, time, and cost of the project (known as the triple constraints of the project) and their impact on quality is represented using the project management triangle.
The role of a project manager is to understand and manage the relationship between these elements of the project using various project management techniques to meet project objectives.
Stages of project management

The moment a project comes into existence, the knowledge of project management starts applying to a project. Project management tries to make the project successful in four simple steps:
- Plan
- Collaborate
- Organize
- Deliver
Let’s briefly discuss the project management stages.
1. Plan
Planning is the first stage of project management where a project manager gathers the project requirements from the stakeholders. Based on the gathered requirements and conversations with the stakeholders, the project manager tries to develop a comprehensive understanding of the project’s objectives, goals, deliverables, key stakeholders, and estimated schedule & budget.
This understanding lays the foundation for a project manager to create a comprehensive plan for the project. This detailed project plan includes defining a project’s:
- Purpose and objectives
- Scope and deliverables
- Success criteria
- Phases, milestones, tasks, and tasks’ schedule
- Resource plan, risk plan, communication plan, and various other project essentials required to guide a project
This is the most important and detailed stage of project management.
The purpose of this stage is to make sure the scope of the project is clearly defined and that necessary resources are assured to work on the defined scope.
Once a project plan is created, the next step is to execute the project plan.
2. Collaborate
It is the second stage of project management, where a project manager delegates tasks to the team and puts the project plan into action. The project team starts working on the tasks and activities as defined in the shared project plan.
In this stage, a project manager coordinates with team members, provides necessary resources, and ensures the team is well-informed about their tasks and timelines.
3. Organize
Project management is not as simple as it sounds on paper: plan, execute, and succeed. It comes with a lot of challenges. Just talk to any project manager around you, they will say projects rarely go as planned. This leads to the need for continuous organization!
Organizing is the third stage of the project where a project manager needs to actively monitor the progress of the project against the project plan and organize the project activities to ensure the project remains on track.
In addition to that, in this step, a project manager practices strict quality control. Deviations are identified and corrective actions are taken to achieve the desired outcomes.
If required, key stakeholders are communicated and updated about the changes in the plan.
4. Deliver
This is the final stage of the project, where project deliverables are finalized and delivered. It officially marks the completion of the project, with final approvals and sign-offs being received from the stakeholders. A final review is conducted by a project manager to evaluate the project and lessons learned are documented.
These four phases of project management provide a structured framework to achieve project objectives within budget and time of defined quality and agreed scope.
Benefits of project management
As we become a little bit aware of project management and understand it, we have learned the importance of project management. It provides a clear direction to the project, breaks a large project into small chunks, defines clear roles and responsibilities, focuses on consistent tracking of the progress, takes a proactive approach to risk management, and encourages transparent communication. This leads to a range of benefits for an organization.
Have a look at some of the most important benefits of project management:
1. Increase success rate
Project management involves clearly defining the scope of the project and creating a comprehensive project plan. It ensures sufficient resources for tasks and plans for risks. This increases the chances of the project’s success.
2. Complete a project on budget and time
Project management breaks a large project into small parts with clearly defined timelines and task owners. This makes it easy to track the progress and manage tasks of the project to complete within budget and time.
3. Reduce the risk of failure
Continuous tracking of the project’s progress helps you identify the deviations early on and predict the bottlenecks. Thus, you can take prompt action to resolve issues before they become bigger project risks.
4. Avoid conflicts
A project plan provides the same information to everyone. This helps bring everyone on the same page. Along with regular meetings, updates, and progress reporting, a project manager can easily clear all the confusion. Thus, the project team stays more informed, on the same page, and involved throughout the project lifecycle.
5. Improve operational efficiency
With a clear roadmap, project team members focus on following the plan and getting work completed. They spend less time figuring out and planning and better manage their time and resources with a clear plan. This helps improve operational efficiency, resulting in savings from unnecessary costs.
These benefits make project management critical for success.
Common myths about project management
Several misconceptions are associated with project management. Here are some of the most common project management myths debunked:
Myth 1: Project management is just for big projects
Many professionals associate project management with complex projects involving large teams and massive budgets. Thus, they are not able to benefit from the knowledge of project management.
But in reality, even small projects can benefit from defined objectives, clear timelines, and structured planning.
Myth 2. You need formal certification to be a successful project manager
Another misconception is that you need formal certification in project management to become a successful project manager. But in reality, most managers are accidental project managers.
Project management is a skill— the ability to plan, organize, communicate, and lead effectively— that anyone with the right mindset and learning attitude can build.
Myth 3. Project management knowledge does not apply to real-world
Many professionals think project management knowledge does not apply to the real world. Indeed, project management cannot guarantee success every time.
Still, it provides you with skills, tools, techniques, frameworks, and knowledge to handle challenges, manage teams, and foster positive relationships with stakeholders.
This increases your chances of project success far more than those who do not apply project management.
Here are some statistics to support our claim:
- Organizations that use project management practices have a 92% success rate in meeting project objectives.
- 67% of organizations provide some form of project management training to increase project success.
- Projects are 2.5 times more successful when PM practices are implemented.
So, what you have decided to choose: misconceptions about project management or the success of project management?






