The aim of a project manager is to complete a project within the approved budget. To do so effectively, a project manager needs to divide the project budget across the lifecycle of the project strategically. Project budget management is a knowledge area focused on the management of the approved project budget.
There are certain things you need to learn for effective project budget management, such as, how to estimate the cost of the project activities so that each activity has sufficient resources and how to calculate the amount for the contingency funds so that the project manager has enough cushion to deal with uncertainties and project risks.
In this chapter, we will explore the concept of project budget management.
What is project budget management?
Project budget management is the process of planning, organizing, monitoring, and controlling the budget of a project. It provides you with a set of tools, techniques, and practices to manage the project budget.
A project manager is provided with a budget at the beginning of the project. It is the role of the project manager to strategically plan and allocate the budget of the project to the various project activities so that a project is completed on time and within the approved budget. Just like time, project cost is one of the key factors deciding the project’s success.
The purpose of project budget management is to complete a project within the approved budget.
Most people confuse project budget management with cost estimation, but it is much more than that. It includes the project’s budget planning, allocation, monitoring and control, and reporting along with the cost estimation.
How to create and manage a project budget?
There are certain steps you need to follow for effective project budget management. Have a look at them.
1. Create a budget for the project
The first step of project budget management is to plan and allocate the allocated budget of the project to create a budget plan for the project. It is the most important step because 28% of project failures are attributed to inaccurate cost estimates. If you do not estimate the cost of the project correctly, it is hard to create a realistic and accurate budget for the project.
What is project budgeting?
Project budgeting is the process of estimating the full cost of the project from the very beginning until the end and allocating funds to each project activity based on the cost estimates and the project’s financial constraints. The purpose is to create a financial plan that serves as a baseline for monitoring and controlling expenditures throughout the project.
Here is a step-by-step guide to creating the budget of the project:
Step 1: Define the scope of the project
The first step to creating an accurate budget for the project is to clearly understand what exactly needs to be done in a project. It can be done comprehensively by defining the scope of the project in detail.
Clearly define the scope of the project. It includes defining project goals, objectives, deliverables, and milestones. You can use a work breakdown structure to clearly define and document the scope of the project at the task level. At the lowest level of the WBS, you can estimate the cost of each task and activity.
Step 2: Estimate the cost of the project
Estimate the cost of each task. There are specific techniques you can use for cost estimation which include:
- Analogous estimation: It uses historical data from similar projects to estimate costs. This technique includes comparing the current project to one or more completed projects with similar scope and requirements, using past project costs as a basis and making adjustments for differences in scale, complexity, or timing.
- Bottom-up estimation: It sums up the individual task costs to get the total estimate. This is a detailed estimation technique that calculates the cost of each project component or activity individually. These detailed costs are then aggregated to determine the total project cost.
- Three-point estimation: It estimates the cost of a task or activity using three scenarios:
- Optimistic (O): best-case cost.
- Most Likely (M): expected cost under normal conditions.
- Pessimistic (P): worst-case cost.
Calculate the weighted average of the three scenarios using the formula:
Estimated cost = (O+4M+P)/6
For example: A task costs:
- Optimistic cost: $9,000
- Most Likely cost: $10,000
- Pessimistic cost: $12,000
Estimated Cost = (9,000 + 4(10,000) + 12,000) / 6 = $10,166.67
- Expert judgment: It leverages the knowledge and experience of subject-matter experts to estimate costs. This technique is often used in conjunction with other methods to validate estimates.
- Parametric estimation: It uses statistical relationships between variables (e.g., cost per unit, cost per square foot) to calculate costs. It identifies key cost-driving variables, multiplies the cost per unit by the total number of units required for the project, and adjusts for any variations or specific conditions.
This helps you create a cost breakdown structure (CBS), which is a visual representation of all project costs that are aligned with the work breakdown structure (WBS).
Step 3: Plan for contingency funds
Every project comes with risks and you need to reserve contingency funds and buffer time to mitigate those risks. Thus, you need to identify and include contingency reserves (for known risks) and management reserves (for unknown risks) in the project estimate. It ensures the budget accounts for uncertainties.
It includes the following steps:
- Analyze potential risks using risk management techniques.
- Identify critical tasks and allocate funds to areas that impact project delivery the most.
- Determine the financial impact of those risks and allocate reserve funds accordingly.
- Ensure high-priority phases receive sufficient financial support.
- Allocate a portion (typically 10-15%) of the budget for unexpected costs or scope changes.
This helps address risks without derailing the project financially.
Step 4: Allocate the funds to the project tasks to plan a project budget
Based on the estimated costs of the project tasks, allocate the project budget to the project tasks. There are many ways to do it effectively in an organized way.
Use the spreadsheet: Create a spreadsheet to structure your budget in a clear format. Use columns for the task name, estimated cost, actual cost, and variance, and use rows for key phases or work breakdown structure elements. This will help you allocate the budget for each phase, milestone, and task of the project and add contingency reserve for the critical tasks.
Use project management software: A Gantt chart in project management software helps you visualize the work breakdown structure on the timeline and map allocated funds to specific tasks, phases, or milestones. You can also add contingency reserve funds on the Gantt chart. This creates a cost baseline to track actual spending and monitor deviations.
Step 5: Organize the costs and budget distribution for clarity and tracking
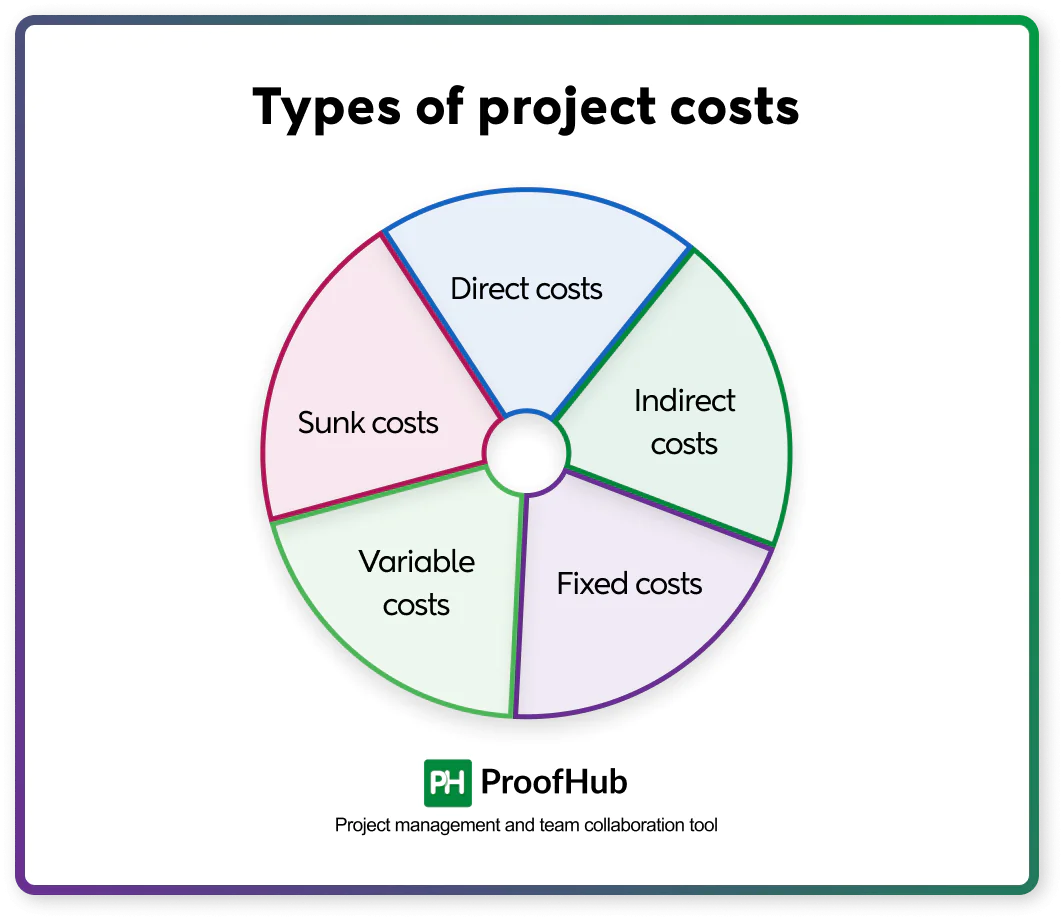
For high-level organization and clarity, you can identify cost categories and distribute the budget:
Types of project costs
- Direct costs: These are the project costs directly related to project activities and are easy to identify. For example, salaries of project team members, materials used to build a product, technology cost, and costs of renting equipment specific to the project.
- Indirect costs: These are the project costs that are not directly related or attributed to the project. It includes costs like administrative costs, utilities, and insurance.
- Fixed costs: These are the project costs that remain fixed throughout the project lifecycle. For example, salaries of the permanent resources assigned to the project, software license fees, and rental fees for office space.
- Variable costs: These are the project costs that vary or occur due to changes in the project scope or timeline. For example, overtime pay, fuel costs, and labor hourly charges.
- Sunk costs: These are costs that have already been incurred and cannot be recovered. It should not be considered when making future project decisions. For example, marketing research and feasibility study costs.
Distribute the Budget
Assign percentages of the budget to major categories such as:
- Human resources: 30%
- Material: 30%
- Tools and technology: 20%
- Administrative costs: 10%
- Contingency funds: 10%
This organization makes it easy to keep track of the project costs. Share the finalized budget plan with stakeholders and team members to bring everyone on the same page.
2. Monitor the project budget
Creating a well-defined, realistic, and accurate budget is half the job done. To ensure a project is completed within budget, a project manager needs to consistently track the utilization of the budget.
Monitoring the project budget involves regular tracking of expenses and comparing them against the planned budget. It helps you identify the deviation from the original budget as soon as it happens or is about to happen.
There are certain techniques used to monitor the project budget. Have a look at them.
Project reports
Project reports are the most commonly used way to track budget utilization. You can create a project report using either project management software or a spreadsheet.
The spreadsheet has various formulas to calculate budget utilization based on the entered data and create various reports to analyze the trends. However, most companies use project management software as it takes very little effort to create detailed reports on the project budget.
It helps you set the estimated cost or planned cost for the project task, record all project expenses as they occur, track the spending in real time, and visualize budget data on the dashboard.
For example, you can create a set of financial fields in ProofHub to plan and track the financial progress of your projects such as planned costs, actual costs, and hourly rates for users and job roles.
These fields automatically calculate essential financial metrics and help you track the budget spent on the task.
Analyze cost variance
Cost variance is the most commonly used metric to track project costs. It is the difference between the budget cost of work performance (BCWP) and the actual cost of work performed (ACWP) of the project.
CV = BCWP−ACWP
- Positive CV = under budget
- Negative CV = over budget
Periodically (weekly or bi-weekly), review the variance between estimated and actual expenses. Or you can simply compare the costs at each project milestone or sub-deliverables to ensure alignment with the budget.
3. Adopt control measures to keep the project budget on track
If you identify the variances in the cost schedule, it is time to adopt control measures to keep the project budget on track. Controlling the budget involves making proactive adjustments to prevent or correct overspending.
Here is a brief explanation of certain measures you can adopt to control your budget effectively:
- Identify variances early: Regularly check for discrepancies between planned and actual costs. Try to find the causes of any variance.
- Reallocate resources: Shift and reassign resources from underutilized areas to tasks that are overspending. It helps you balance workloads and avoid overtime costs.
- Optimize processes: Streamline workflows to reduce delays and save costs.
- Use contingency reserves: Mitigate risks using contingency reserves for unavoidable expenses.
- Adjust the project plan: Adjust the project timeline, prioritize high-value deliverables, or reassess milestones and redistribute funds accordingly.
- Communicate with stakeholders: If budget overruns are unavoidable, inform stakeholders immediately about budget challenges. Provide solutions and revised projections to maintain trust and transparency.
- Set up a formal request for scope changes: Prevent unauthorized changes to the project scope. Make sure approval is required for all scope changes and cost estimates are revised based on the new requirements.
Review lessons learned and document what worked and didn’t to improve future budgeting.
Importance of project budget management
Project budget management provides you with a clear roadmap on how the project costs are determined, the project budget is allocated, monitored, and controlled, and project risks are managed. It makes sure every project activity has sufficient funds to complete a project on the budget. This leads to the following benefits for a project:
Completes a project on time and budget
Inaccurate initial cost estimates can lead to budget overruns and unrealistic deadlines may force teams to spend more on additional resources. Using cost estimation techniques to accurately predict the cost, developing a realistic project schedule with input from team members and stakeholders, and planning for unexpected expenses and potential delays with contingency reserve and buffer time in the schedule ensure every project task has sufficient resources to complete on time and budget.
Prevent scope creep
Uncontrolled changes or additions to the project scope increase costs. It often occurs due to poorly defined scope or a lack of change control processes. Defining the project scope comprehensively, documenting it in a scope statement, and implementing a formal change control process where all scope changes require approval and budget adjustments ensure necessary resources are secured to incorporate new changes.
Create a shared understanding
Miscommunication among team members and stakeholders can lead to unclear cost expectations or unapproved spending. Using standard documents like cost breakdown structure, Gantt chart, risk register, and standardized metrics and budget reports that highlight variances, risks, and forecasts creates a shared understanding for everyone.
Common challenges in budget management and solutions to overcome
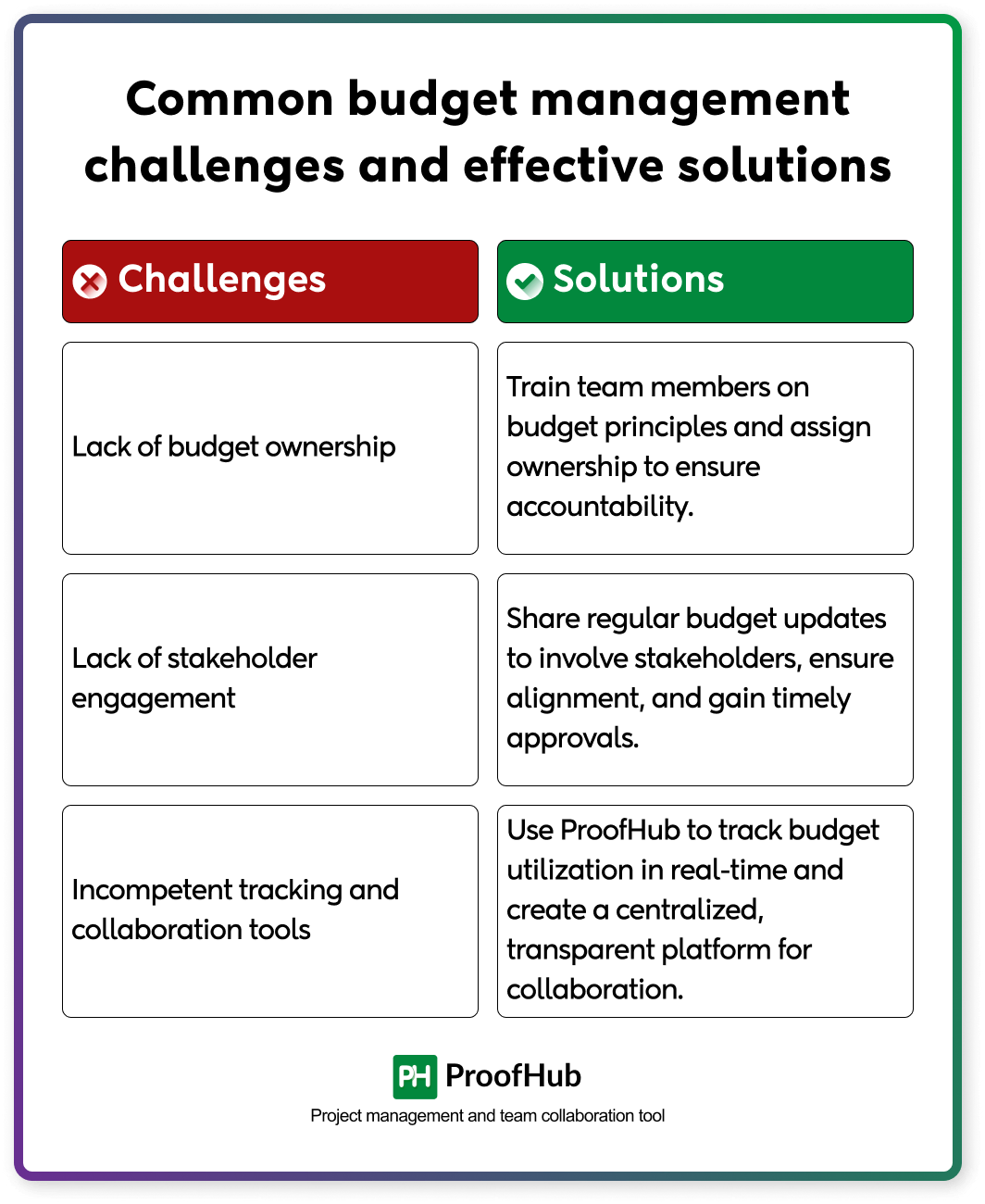
Despite creating an effective budget plan, there are some challenges you are going to face. Have a look at the common challenges and proactive measures to resolve those challenges.
- Lack of budget ownership: Most professionals think budget management is entirely the responsibility of the project manager. This often leads to overspending. Train team members on basic budget management principles to build accountability. Assign budget ownership to specific team members or department heads for their areas of responsibility. Without clear accountability, team members may not prioritize cost control.
- Lack of stakeholder engagement: If the budget status is not regularly updated or shared or stakeholders do not fully understand the budget, it may lead to delayed feedback or approvals can disrupt financial planning. Thus, stakeholders should be involved throughout the process to ensure alignment and buy-in. Provide transparent financial updates to maintain trust and encourage collaboration.
- Incompetent tracking and collaboration tools: Relying on outdated or manual tracking methods can lead to errors or delays in identifying budget issues and a lack of standardized collaboration tools creates miscommunication among team members and stakeholders. This leads to the project budget getting off track. Thus, use project management and team collaboration software like ProofHub, Wrike, and Jira to track budget utilization in real-time and create a centralized, standardized, and transparent place for team collaboration.
Modern project management software comes with built-in budget management and team collaboration features. Let’s understand how tools like ProofHub help you manage project budgets.
ProofHub: Software for project budget management

ProofHub is an all-in-one project management and team collaboration software that helps you with project budget management by providing you with tools to create, track, and manage project budgets.
- Plan the budget and allocation throughout the project: ProofHub allows you to break a project into major deliverables, sub-deliverables, and tasks in alignment with the work breakdown structure. You can set the estimated cost and time of the project tasks. This makes it easy to divide the project budget across the lifecycle of the project.
- Identify and manage risks with Gantt chart: ProofHub comes with powerful Gantt chart software where you can visualize the entire project plan with tasks mapped to the timeline, set and visualize the dependencies, define the milestones, and add contingency funds and buffer time with constraints. This makes it easy to track the progress and corresponding budget utilization.
- Budget utilization tracking with reports: with ProofHub project reports, a project manager tracks the budget spent on tasks with a planned budget. This helps you make decisions based on the data in real time.
- Centralized task management: ProofHub provides a centralized task management platform for a project manager to track the status of each project task in multiple project views such as Board, Table, and Calendar. This helps a project manager track task status, reallocate resources, and add priority to complete the task on time and budget.
- Collaborate with stakeholders: ProofHub offers plenty of collaboration features which makes it easy for a project manager to collaborate with team members and stakeholders. For example, a manager communicates with the project team using project discussions and reaches out to individual team members with a 1:1 chat. It makes it easy to prior.






