Just like time and budget, there is another factor that determines the success of the project, it is project quality. If a project does not meet quality requirements, project sponsors or the project client will not accept the project deliverables, even if it is completed on time and within budget. Thus, a project is deemed a failure because it needs rework.
It is the role of a project manager to make sure a project fulfills its quality requirements along with completing it on time and within budget.
Project quality management is a knowledge area that provides you with the knowledge to manage the quality of a project from beginning to end. In this chapter, we will look at the processes of quality management in project management and the steps to implement project quality management to a project.
What is project quality management?
Project quality management is the process of defining the project quality requirements, monitoring project quality, and controlling the quality of project activities to ensure project deliverables meet the set requirements. It determines the success of the project by ensuring a project meets stakeholders’ and end-users’ quality expectations.
Project quality management involves three primary steps to ensure project quality:
- Quality planning
- Quality assurance
- Quality control
1. Quality planning
Quality planning in project management involves identifying the project quality requirements and standards for the project and determining how to achieve them. It includes creating a project quality management plan.
2. Quality assurance
Quality assurance in project management is the process of making sure quality-related activities and processes defined in the quality planning stage are in place to maintain quality. It includes performing activities mentioned in the checklist and auditing the quality control measures to ensure appropriate quality standards.
3. Quality control
Quality control in project management is the process of monitoring and recording results of executing quality activities to assess performance, recommend necessary changes, and take corrective actions to solve an issue. It involves an operational process of not preventing problems, which is done in the quality assurance.
Importance of project quality management
Project quality management plays a vital role in ensuring the project’s success by creating a well-defined plan to manage the project quality from beginning to end. It defines the quality requirements and standards for a project’s deliverables, measuring the quality of the project activities based on those agreed metrics, and taking corrective measures if a project deliverable deviates from its quality standards. This leads to the following list of benefits:
1. Ensure quality
A well-designed project management quality plan outlines the quality requirements, and activities to ensure meeting quality standards and quality control measures. Thus, everyone knows about the quality expectations, roles and responsibilities, quality checklists, and plan of action if something goes south. This improves operational efficiency, promotes collaboration, and streamlines quality management operations. In addition, quality improvement initiatives improve the quality of the project deliverables produced.
2. Reduce costs
Project quality management requires you to perform some extra tasks and quality checks from time to time which costs extra money and resources. However, the absence of quality management projects leads to major losses. It is because you are not able to identify and resolve issues early on and you have to rework again and again which can derail your project schedule, scope, and cost. The cost of preventing mistakes is generally much less than the cost of correcting them when they are found by inspection.
3. Increased productivity
When teams are constantly fixing mistakes, it can be demoralizing and hinder overall productivity. Quality management fosters a culture of ownership and continuous improvement. By empowering teams to take pride in their work and focus on delivering quality results, you’ll see a boost in morale and overall productivity. This positive work environment leads to a more engaged and motivated workforce.
4. Mitigated risks
Project quality management isn’t just about deliverables; it’s about proactively managing potential risks. Regular quality checks throughout the project lifecycle help identify and address potential problems early on. This enables taking preventative measures, minimizing the impact of unforeseen issues, and ensuring the project stays on track. It helps catch issues early to avoid costly rework and delays.
5. Ensure customer satisfaction
A project quality management plan includes a clear description of the project’s end goals. By applying quality project management, you can create products that satisfy the client’s needs and quality expectations. This improves client satisfaction, reduces the risk of project failure, and improves brand image when your customers take notice you are delivering quality work.
How to implement project quality management in a project?
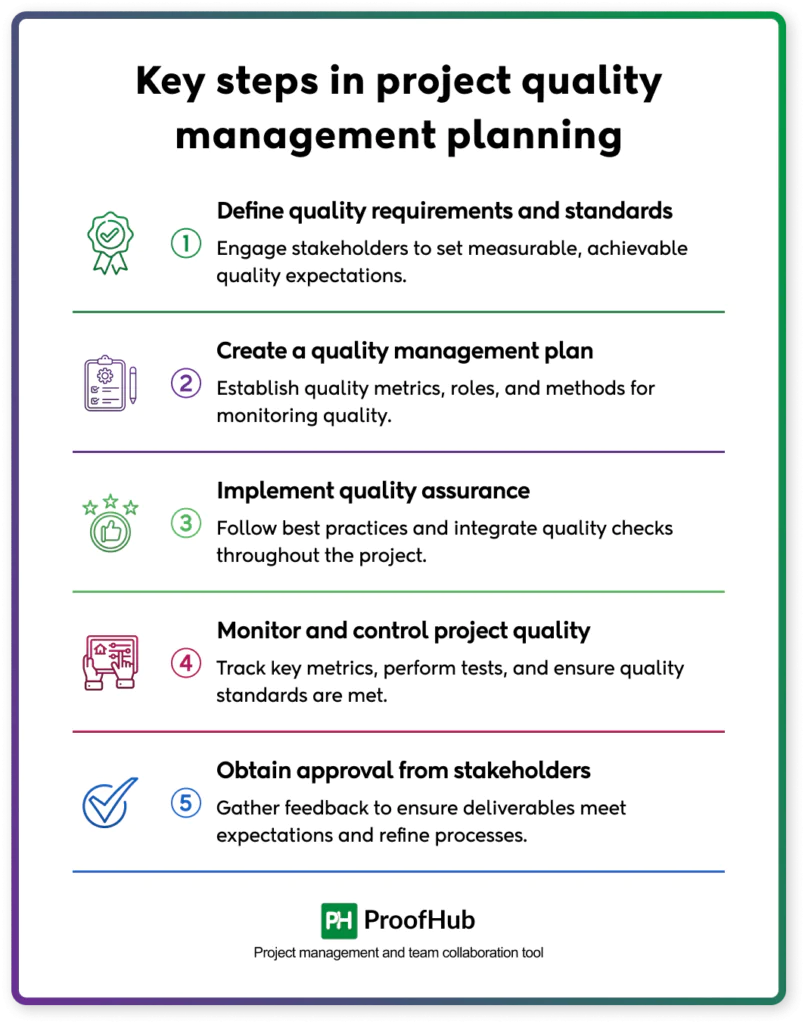
There are certain steps you need to follow to implement project quality management to a project. Have a look at them.
1. Define quality requirements and standards
The first step to applying project quality management to the project is defining and setting quality standards in projects. To do so, you need to gather the project client and sponsor’s requirements, consider the industry-specific quality standards, and take into account the end-users expectations. This will help you set comprehensive quality standards and requirements for the project.
Here is how to do it:
- Engage with clients and stakeholders to identify their needs and quality expectations and translate these expectations into clear, measurable quality requirements.
- Take into account the industry standards and metrics such as ISO standards, PMBOK guidelines, and customer satisfaction.
- Interview end-users to define the quality requirements.
You can use the SMART framework to write the project quality requirements, project quality objectives, and quality management standards. SMART stands for specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound.
These requirements should be documented and approved by the stakeholders to create a quality management plan.
2. Create a quality management plan
The next step is to create a project quality management plan. It includes defining quality metrics, measures for quality monitoring and control, roles and responsibilities of each individual, and tools and techniques for quality management.
Here is what you need to do to create a quality management plan:
- Define quality metrics: Identify metrics to define how you are going to measure the quality. The most commonly used quality metrics in project management are: project status, cost performance index, earned value, resource utilization, budget utilization, cycle time, and cost variance. Choose the metrics as per your project needs.
- Identify roles and responsibilities: Define who is responsible for quality assurance (QA) and quality control (QC) activities. If necessary, involve third-party quality experts or auditors.
- Define the acceptance criteria: Acceptance criteria are probably the most important factor in project quality management. It is defined as the conditions that must be satisfied for a product deliverable to be accepted. Clearly specify conditions for deliverables to be approved by stakeholders.
- Design workflows: Include quality checks at key stages of the project in a workflow such as design, development, and delivery.
- Define methods: Define what methods you are going to use for checking deliverables at key project stages such as review and testing. Allocate sufficient time and budget for quality-related activities.
- Audit regularly: Schedule periodic reviews to ensure compliance with the quality plan.
- Create a risk management plan for quality: List potential risks affecting quality and plan mitigation measures to address risks. For example, for missed deadlines add buffer time.
- Quality reporting: Define how quality updates will be shared with stakeholders. For example, status reports and dashboards. Set dates for regularly reviewing quality progress with stakeholders and discussing corrective actions if necessary.
- Define tools and techniques: Define the tools you will use for project quality management such as flowcharts, control charts, and checklists. Use standard frameworks like Six Sigma, TQM, or Lean for designing quality processes and software like ProofHub, Jira, and Wrike for implementing quality processes.
The next step is to implement the project quality management plan. It involves quality assurance, monitoring and control, and improvement.
3. Implement quality assurance
Implement a project quality management plan by making sure every measure is implemented as defined. You can use tools like the Gantt chart to integrate the quality management plan into the project plan. This will provide you with a clear idea of when to perform each quality activity.
Employing the best practices for quality management such as:
- Periodically assessing whether the processes are being followed as planned.
- Creating a checklist to follow.
- Designing a workflow with reviewers added at crucial points.
- Using proactive quality assurance techniques to ensure quality.
This helps you identify and address inefficiencies in workflows and fosters an environment where team members value and prioritize quality.
4. Monitor and control the project quality
To ensure project quality is maintained, a project manager needs to regularly track certain parameters for the quality and perform quality tests at critical steps. Project quality monitoring and controlling include tracking progress and inspecting deliverables at key stages of the project to ensure compliance with quality criteria.
Here is what it includes:
- Measuring key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure performance against set quality metrics as defined in the plan.
- Performing usability testing or peer reviews depending on the type of project.
- Implement corrective actions to resolve issues and preventive measures to avoid recurrence.
- Apply iterative improvements to project workflows and methodologies to optimize performance.
You can use tools like control charts, project network diagrams, affinity diagrams, matrix diagrams, and statistical analysis to evaluate quality.
- Control chart: A control chart is a visual tool used to monitor whether a process is consistent (in control) over time. It helps track performance metrics and detect variations that might indicate quality issues. The chart displays:
- A central line: Represents the average value of the data being measured.
- Upper and lower control limits: Define the acceptable range of variation.
Example: If you’re monitoring production time, the limits might be “10 minutes minimum” and “15 minutes maximum.”
Data points are plotted on the chart over time. If the points stay within the limits, the process is under control. Points outside the limits signal a problem needing investigation.
- Project network diagram: A project network diagram is a chart that helps teams visualize the activities that need to be completed throughout a project. It talks about the schedule and sequence of all activities of a project and uses the boxes and arrows to depict the flow of tasks.
- Affinity diagram: An affinity diagram is a tool that allows you to organize and categorize ideas, thoughts, or information about a project in groups with common relationships. It is a great tool for quality project management as it allows you to identify quality requirements for similar activities.
- Matrix diagram: A matrix diagram serves as a tool to establish relationships between data sets. In the context of quality management, it establishes relationships between deliverables and quality standards. This is a great tool for quality assurance as for each deliverable you have a set of quality standards to match.
- Statistical analysis: Statistical analysis involves collecting and analyzing data to identify patterns, trends, and variations. It helps make informed decisions about quality improvements. It includes three types of analysis techniques:
- Descriptive statistics: It summarizes data using averages (mean), medians, or percentages.
- Inferential statistics: It makes predictions or test hypotheses based on sample data.
- Sampling: It inspects a subset of items rather than all items to save time while still gaining insights.
5. Obtain approval from stakeholders
The last step for project quality management is to obtain approval from the key stakeholders on the project deliverables. If you have documented the project requirements comprehensively, gained approval on the requirements before the execution, and followed the checklist to ensure deliverables meet all documented quality requirements, there are chances stakeholders will approve the deliverables. But it is advised to expect minor changes.
Present the final product or service to stakeholders for acceptance. Gather feedback from stakeholders and clients to understand their satisfaction levels. Make adjustments if needed to ensure deliverables meet expectations. Encourage continuous feedback from teams, stakeholders, and customers to refine processes and improve outcomes.
In the end, conduct a post-project quality review to identify successes and areas for improvement and document lessons learned for future projects.
Tools for quality assurance and control
Project quality management plan is incorporated into the project plan to ensure the quality of the project. Project management software is used to implement the project quality management plan. It provides you with a wide range of tools for quality management to implement the project quality management processes: planning, assurance, and monitoring and control.
To get an enhanced understanding, we will explain how you can use ProofHub for project quality management.
- Identify the project quality requirements with discussions: ProofHub allows you to facilitate group discussions with project discussion boards. You can involve project sponsors, clients, and key stakeholders and can document the entire discussion to clarify project quality requirements.
- Create a project quality management plan: ProofHub allows you to break the project into major deliverables, sub-deliverables, and tasks and sub-tasks. You can create a custom workflow with ProofHub and add quality control steps at the key stages of the workflow. With a built-in chart, you can perform the quality planning of the project comprehensively by visualizing the project plan on a timeline.
- Centralized task management: With ProofHub task management, you can create tasks for Quality Assurance and Quality Control and assign these tasks to the respective team members. Having all the tasks in a centralized place makes it easy to track progress.
- Track the progress: With ProofHub reports, you can track the project performance and quality metrics. Reports provide you with real-time data in an organized way for analysis
- Collaborate with a team: ProofHub provides you with a suite of collaboration features to collaborate with the team and implement the project plan. You can communicate with team members using chat, share files, and participate in group discussions.
Our team of project management experts will take you through a live demo to showcase how you can manage the project quality with ProofHub.






