Goal setting is an indispensable part of project planning, but it is not about setting any goals— it’s about setting SMART goals and milestones that truly drive success.
Through my experience working closely with project managers, especially first-time or accidental managers– I’ve noticed a common challenge, ‘setting clear, achievable objectives’. Alongside, I have also learned one fundamental truth that effective project management goes beyond defining goals only to provide clarity and drive real results.
And when projects get bigger, more complicated, and more ambitious, it’s even more important to go beyond the budgets, schedules, and fundamental specifications. I need to think strategically and set goals that keep everyone aligned and focused.
That’s the reason I am such a strong advocate for SMART goals as they deliver substantial results-focused and aligned teams, streamlined project processes, and quality project deliverables.
So, whether you’re managing a team of fifty or five, SMART goals provide the structure you need to deliver successful projects, time and time again. But here let’s be real by knowing that SMART goals aren’t always as straightforward as they sound.
In this article, I’ll show you why SMART goals are crucial to you as a project manager and how you can establish them to transform your project planning process. By the end, you will have a clear understanding of how SMART goals work for you and help you turn all those vague ambitions into actionable success. Let’s understand.
What are SMART goals?
In project management, SMART is an acronym that stands for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-bound. It mainly refers to the criteria of goal-setting in a way that allows teams to focus their efforts and work in alignment to achieve the desired vision easily.
The term was first coined by George T. Doran, a consultant, president, and former director of Corporate Planning for Washington Water Power Company, Spokane, Washington in 1981 in a paper, titled “There’s a S.M.A.R.T. Way to Write Management’s Goals and Objectives”.
He outlines that, “when it comes to writing effective objectives, corporate officers, managers, and supervisors just have to think of the acronym SMART. Ideally speaking, each corporate, department, and section objective should be: SMART
Notice that these criteria don’t say that all objectives must be quantified on all levels of management.”
He goes on to contradict the most popular perception of SMART goals, stating that, “It should also be understood that the suggested acronym doesn’t mean that every objective written will have all five criteria.”
The basic ideology behind this concept is to increase effectiveness and efficiency at all stages of project planning, monitoring, and execution towards ensuring successful completion and tangible outcomes.
Let’s discuss the different components of SMART goals with examples and explain their role in ensuring project success:

1. Specific: Make sure your goals are clearly defined
The first component of SMART goals is ‘specificity’. A vague or broad goal not only leads to confusion but also causes misalignment and lack of direction. For project goals to be effective, they should be clear, well-defined, and easy to comprehend for everyone in the team. The goals should be such that they answer the five W’s (who, what, when, where, and why) regarding the project. Take a look at the two examples below:

Unclear goal: Gather more traffic to the website.
Specific goal: Increase organic traffic by 2,000 visitors per day. (clear goal)
Clearly, the second goal is very specific and to the point and is more likely to generate better results as compared to the first goal. Also, a specific goal like this not only sets clear expectations but also provides a roadmap for action, making it easier to track progress and make necessary adjustments.
2. Measurable: Make sure your goals are trackable
The second component of SMART goals is ‘measurability’, which ensures that the project outcome should be quantifiable or measurable. Having a metric in place provides project managers the ability to measure their overall progress and performance. This helps project managers track progress, spot inefficiencies, make informed decisions, and optimize efforts.
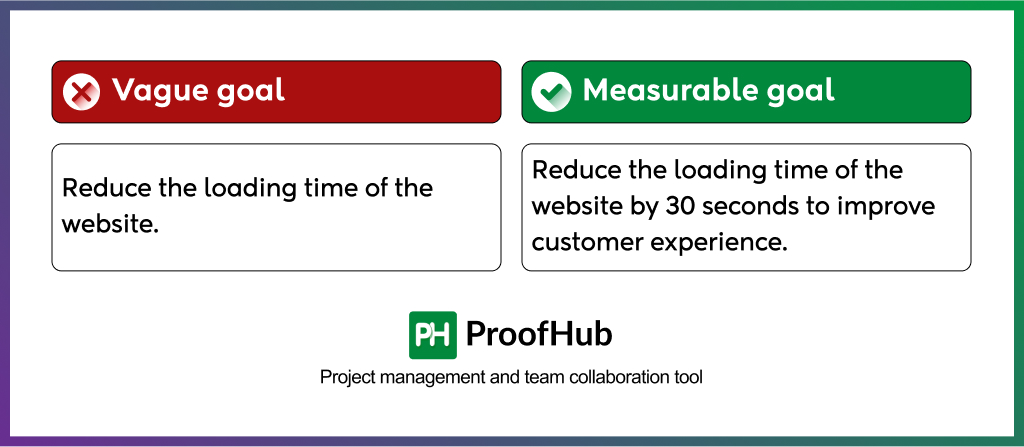
Vague goal: Reduce the loading time of the website.
Measurable goal: Reduce the loading time of a website by 30 seconds to improve customer experience.
Unlike the first goal, the second goal defines a measurable outcome. If you can tack it, you can improve it.
3. Achievable: Make sure your goals are attainable
The third component of SMART goals is about ‘achievability’, which means all the goals, objectives, and milestones included in a project should be attainable. And in doing so, it’s essential to consider factors like constraints of time, resources, costs, and unexpected risks. Even though your team members should put in their best efforts towards project completion, it should not demand every ounce of their energy, leading to frustrated teams and failed projects.

Unrealistic goal: Double our sales in one week.
Attainable goal: Increase sales by 15% in the next quarter by implementing a targeted marketing campaign.
The second goal is more realistic and can be easily achieved in the desired time slot.
4. Relevant: Make sure your goals are aligned
The fourth component of SMART goals is ‘relevance’. The basic ideology behind the concept is to figure out if the goal established aligns with not just the project’s overall objectives but the organization as well. Also, client requirements, team priorities, and resource availability are key factors that influence relevance. It is better to focus on goals that contribute to project achievement.

Off-track goal: Attend a project management conference by June 30, 2025 (unrelated to our e-commerce project).
Relevant goal: Launch the new software feature by March 15, 2025, with all tests completed and documented.
Clearly, the first goal might be interesting, but it doesn’t contribute to the project’s success. The second one directly impacts the deliverables and aligns with business needs.
5. Time-bound: Make sure your goals have a deadline
The fifth component of SMART goals is ‘time-boundedness’. This indicates that every project goal has to have a specific timeframe by which a project outcome, be it failure or success, should be evaluated. Making time-bound goals creates accountability and urgency, allowing team members to prioritize effectively, manage resources, and stay focused to deliver results. You can use the Critical Path Method (CPM) to schedule tasks and estimate realistic duration so that deadlines don’t suffer.

Open-ended goal: Let us fix all the open bugs.
Time-bound goal: Fix critical bugs by the end of this weekend by all means.
Of course, the second goal is specific, time-bound, and has clear targets that encourage team members to work in alignment so that every step forward pushes the project to the finish line.
Why are SMART goals important for project managers?
Project managers are the architects who create a strong plan for guiding a project from initiation to completion. From deciding on objectives to facilitating understanding amongst stakeholders, they control the entire process without being directly involved in the tasks themselves.
“The establishment of objectives and the development of their respective action plans are the most critical steps in a company’s management process.” – George T. Doran
The importance of SMART goals in project management and for project managers goes beyond creating simple and structured guidelines for teams. It is a skill you must hone to redefine the way you manage projects.
Explore the list of 14 key project manager roles and responsibilities for better success
Here are a few more reasons how SMART goals can help project managers:
- Define clear expectations: SMART goals enable you to communicate realistic and achievable requirements, giving teams the clarity they need to stay focused. It is this sense of direction that motivates even the most skeptical of team members to confidently take up tasks and managers to hold them accountable for their progress and results.
- Provide direction and structure: SMART goals enable project managers to give clear and specific guidelines to team members. This allows team members to own up and assess their work toward the realization of project objectives. Freeing up project managers the time they otherwise would have wasted looking into the nitty gritty of projects.
- Better resource allocation: SMART goals facilitate the accurate identification and allocation of resources, ensuring alignment with project objectives. Be it human, technical, material, or financial, you can plan and invest resources correctly in the areas where their potential is maximized. Also, it prevents the over or under-utilization of resources that can hinder progress.
- Better performance tracking: When you work on establishing the M of SMART goals, you define a measurable metric that can help you track progress and performance effectiveness. This way you can easily spot bottlenecks, identify inefficiencies, and resolve issues injurious to your project’s health.
- Manage risks proactively: Clear, measurable, and achievable goals set a transparent space for project managers to monitor risks effectively. The moment you spot any disruptions in the project flow, you can immediately intervene to adjust strategies before they shape up to cause significant delays and disrupt momentum.
- Improve decision-making: With every parameter thought upon when establishing SMART goals, project managers can make decisions confidently, knowing their decision is in the best alignment with project objectives and outcomes. And why not? After all, you get measurable objectives to back your decisions with clarity and purpose.
How to set SMART goals?
Goal setting isn’t limited to just jotting your objectives down on a paper or a project management software and assigning them to project teams for accomplishment. Rather it is a complete process that comprises multiple other factors, including thoroughly articulating clear expectations, involving stakeholders in the process, defining milestones, and ensuring alignment.
And that’s why project managers should have a comprehensive understanding of the goal-setting process. So, here is the 6-step strategy that I and my team follow to set SMART goals.
You can take note of this to ensure project success:
1. Identify your vision
Before you start to establish SMART goals, make sure to contemplate the broader purpose of the project and determine if it aligns with your company’s long-term values. This vision provides a direction for your team while allowing you to assess possible impacts (both positive and negative) it can have on your organization.
An example of a well-defined vision is:
“Implement a refined marketing strategy to broaden our customer base and promote sustainable business growth by connecting with new demographics and improving outreach.’
2. Break down the vision into SMART components
Once you have clarity on your vision, you can systematically determine if the project’s vision can stand up to the SMART criteria. Let’s break it down below:
Specific
- What? Launch a new marketing strategy targeting customers through digital platforms.
- Why? To tap into an untapped market segment and increase brand visibility.
- How? Focus on social media campaigns and targeted paid ads on online platforms.
- What? Introduce a tailored marketing strategy targeting younger demographics (ages 18–25) via digital platforms.
Measurable
- Increase the number of new customers by 20% within 6 months.
- Secure 200 leads per campaign.
Achievable
- Allocate a dedicated budget for ad spend, influencer collaborations, and social media management.
- Assign specific roles to the marketing team, such as ad specialists and content creators, for smooth execution.
- Analyze competitor performance to determine realistic benchmarks.
Relevant
- This strategy aligns with the company’s growth goals by increasing the customer base and revenue.
- Reaching a younger audience supports long-term brand sustainability.
Time-bound
- Finalize the strategy by February 2025.
- Launch campaigns by March 2025.
- Track progress and achieve defined targets along the way.
3. Build an effective framework
If defining SMART project goals is the first step to … a project, drafting a solid framework is the next step that could seal the deal for a successful project.
Build a clear plan that entails everything required for SMART goals execution. This can include tools, timelines, workflows, processes, communication channels, and roles to reduce confusion and increase efficiency.
A framework provides a structure that encourages common understanding, keeps team members on track, and assures accountability for consistent performance and improvement.
Explore our guide for a comprehensive understanding of the project management framework
4. Identify high-impact initiatives
After you have set up and created the goals, identify the tasks, actions, and dependencies that are going to provide the most value and contribution towards achieving your project goals. This will help align high-impact initiatives with the long-term goals and vision of the organization while eliminating low-priority tasks.
Spending time on tasks that do not add any value – directly or indirectly, will bring nothing significant and constructive to the project. So, make it a rule to identify and prioritize high-impact tasks to capitalize on your team’s potential the right way without stretching them out too thin.
5. Get the right people onboard
A project’s success or failure greatly depends on the ability, skills, and experience of project members – individuals responsible for the execution of a project.
As a project manager, it’s your responsibility to delegate tasks based on strengths, motivate them when necessary, and equip them with the required resources to execute project plans successfully.
Apart from just hiring skilled and enthusiastic team members, make sure to groom the existing workforce with the relevant skill training and certifications to make them valuable assets and smart working professionals.
Learn 11 effective tips and strategies to build a high-performing team
6. Review and adjust
Lastly, ensure that there is a progress check and evaluation of performance to SMART goals; this can help identify whether the project is on track or has deviated into something else from the expected set.
You can also involve your team and other stakeholders to gather their feedback and valuable insights on performance, ensuring that the strategy stays relevant and delivers on everyone’s expectations.
Don’t be afraid to redefine your goals, timelines, or approach if it ensures better outcomes.
Discover how you can enhance your performance review process to ensure remarkable results
What are the benefits of setting SMART goals?
Organizations do set goals before initiating a project, but when they make sure these are SMART, the effectiveness of the entire process improves significantly, limiting the possibility of the project hitting rock bottom.
Apart from this, the following are the benefits of setting SMART goals:
- Increased efficiency: When you bring clarity to the team by setting SMART goals that stand strong on every parameter, teams spend more time working than looking around for instructions and clarifications. Knowing what is expected of them, they can make concentrated efforts and achieve more without wasting their time guessing what to do and how to do it.
- Better alignment: SMART goals act as a blueprint that brings everyone on the same page. This means everyone knows what to do, what task the other team member is doing, and how their aligned efforts contribute to achieving project objectives. Not only this, a deliberate effort goes into establishing the relevance of the goals in the initial stage, ensuring the organization’s broader vision stays intact.
- Minimizes scope creep: As we know unnecessary and unexpected circumstances are beyond our control and can derail even a well-laid project. However, well-defined goals protect the integrity of the project against these deviations as much as possible. Clearly defined boundaries, deliverables, and expectations ensure progress stays on track despite the challenges that arise.
- Boost team engagement and collaboration: Gaining a shared knowledge of the set objectives serves as a team-building activity. This promotes productive teamwork as it entails healthy discussions, constructive feedback, and mutual contributions in producing excellent results.
- Adaptability and sustainability: SMART goals focus on consistent, measurable progress and regular reviews, allowing teams to continually improve and adjust strategies. It encourages them to look for innovative solutions and eliminate inefficiencies. This winning framework can further be used in the future for other projects.
- Improved outcomes: Lastly, SMART goals bring structure, clarity, and focus from the beginning, which eliminates the scope for redundancies, inefficiencies, and miscommunications. Of course, you need to keep other factors like resource availability, timeline management, and team capacity in check to ensure timely and high-quality deliverables.
Common challenges in setting SMART goals
Regardless of how beneficial SMART goals can prove to be, implementing them may have its own set of challenges that must be tackled carefully by project managers. Here are some common obstacles that may come your way:
- Poor planning: It is one thing to set SMART goals and another thing to establish them with proper understanding, research, and foresight of the project scope. Not accounting for the full scope, obstacles, and benefits, can lead to goals that may look good on paper but not in practice. This makes even the most precise goals you have worked so hard to define ineffective or ambiguous outputs.
- Unrealistic timeframes: Setting goals with tight deadlines or expectations, that are too lofty to achieve, can cause teams to stretch their work hours, leading to burnout and decreased morale. And if you think it is okay for your team to work this way in the name of being productive, be prepared to deal with compromised work quality and deliverables. Unrealistic timeframes diminish the long-term sustainability of your team.
- Resistance to change: When you shift your focus from setting just goals to SMART ones, you introduce changes in processes, workflows, or even working styles. This may cause some resistance from team members or stakeholders, resulting in delayed implementation or half-hearted adoption. People naturally resist change when forced without clear communication and buy-in.
- Setting rigid or over-ambitious goals: Often at times, project managers end up setting goals that are too ambitious or too rigid in terms of flexibility. This often leaves no scope for adjusting to unforeseen changes and, hence, causes frustration and discouragement among teams, lowering their morale and confidence and leading to a negative impact on the overall project.
- Not accounting for resource availability: It is one of the most common mistakes project managers make when setting SMART goals. Not taking into account their resources’ availability, capacity, and workload can leave even the smartest goals astray. And that’s pretty obvious. You can’t expect timely and quality results if you lack sufficient manpower, tools, or budget—or if you overcommit them to tasks beyond their capacity.
- Maintaining consistency: Regardless of how well you have ensured the measurable aspects of the SMART goals, if you fail to consistently track progress throughout the project or simply forget or let it go, you cannot ensure consistency throughout the entire project lifecycle. Without regular reviews, adjustments, and course corrections, even well-set goals may drift off track.
Examples of SMART goals for project managers
SMART goals are not limited to specific aspects but can be applied to almost all realms of project management. All it requires is for you to have a clear understanding of the project’s needs and a thoughtful approach to goal-setting.
Below I have mentioned two examples of weak goals and their dissection into SMART goals:
Example 1: Improving team productivity
- Weak Goal: “Improve team productivity.”
- SMART Goal:
S – Increase team productivity
M – Increase it by 15%
A – Achieve it by introducing new tools and training sessions
R – It will improve project outcomes, promote teamwork, and maintain efficiency
T – It has to be done by the end of the third quarter
“Increase team productivity by 15% by the end of Q3 2025 by implementing new collaboration tools and conducting monthly training sessions.”
Example 2: Risk mitigation
- Weak Goal: “Reduce project risks.”
- SMART Goal:
S – Identify and mitigate 90% of project risks
M – Mitigate 90% of project risks
A – Achieve it using proper tools and responsible individuals
R – It will ensure smoother project execution by reducing delays, budget overruns, and quality issues.
T – It has to be done by March of this year
“Identify and mitigate 90% of project risks during the planning phase by March of this year, using a risk assessment matrix and assigning ownership for each identified risk.”
What is the difference between SMART goals and objectives?
SMART goals and objectives, which are often confused with each other, are two different concepts that complement one another. Where SMART goals are the prime results based on the SMART criteria you aim to achieve, objectives are smaller, actionable steps taken to achieve that goal.
| Aspect | SMART Goals | Objectives |
| Focus | Broad primary outcome | Concrete steps to achieve the result |
| Scope | High-level and overarching direction | Narrow, detailed, and task-oriented. |
| Timeframe | Longer-term, spanning the project lifecycle. | Shorter-term, linked to specific tasks or phases. |
| Measurement | Clearly defined metrics to track overall success. | Milestones or checkpoints that lead to the goal. |
| Example | “Increase sales by 20% within 6 months.” | “Launch a social media campaign within 4 weeks.” |
Conclusion
It is easy to feel confident and find nothing problematic in your current approach to setting goals – until you hit dead ends and find yourself stuck, unable to move forward.
No matter how experienced you are, trust me when I say, effective goal-setting makes a difference in your project’s success. As a project manager, the ability to set SMART goals gives you an undeniable edge over those who don’t.
This is a skill you can develop, regardless of where you are in your career. With a bit of practice and willingness to make hit-and-trials, you can refine your approach to setting goals. Try, evaluate, and adjust until you nail the game to setting SMART goals.
FAQs
Can SMART goals help manage team performance?
Yes, project managers can use SMART targets to better manage and improve team performance. By creating defined roles and expectations, deadlines and milestones, and ensuring alignment with broader corporate objectives, project managers enable teams to work with clarity and focus. Teams are inspired to take ownership, prioritize tasks, and collaborate effectively to make project a hit.
How can SMART goals improve decision-making in projects?
SMART goals and objectives, which are often confused with each other, are two different concepts that complement one another. Where SMART goals are the prime results based on the SMART criteria you aim to achieve, objectives are smaller, actionable steps taken to achieve that goal.

